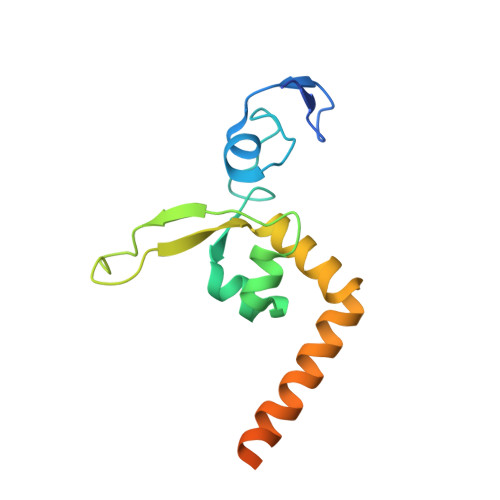
New structural insights into the recognition of undamaged splayed-arm DNA with a single pair of non-complementary nucleotides by human nucleotide excision repair protein XPA.
Lian, F.M., Yang, X., Jiang, Y.L., Yang, F., Li, C., Yang, W., Qian, C.(2020) Int J Biol Macromol 148: 466-474
- PubMed: 31962067
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.169
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6LAE - PubMed Abstract:
XPA (Xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group A) is a core scaffold protein that plays significant roles in DNA damage verification and recruiting downstream endonucleases in the nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway. Here, we present the 2.81 Å resolution crystal structure of the DNA-binding domain (DBD) of human XPA in complex with an undamaged splayed-arm DNA substrate with a single pair of non-complementary nucleotides. The structure reveals that two XPA molecules bind to one splayed-arm DNA with a 10-bp duplex recognition motif in a non-sequence-specific manner. XPA molecules bind to both ends of the DNA duplex region with a characteristic β-hairpin. A conserved tryptophan residue Trp175 packs against the last base pair of DNA duplex and stabilizes the conformation of the characteristic β-hairpin. Upon DNA binding, the C-terminal last helix of XPA would shift towards the minor groove of the DNA substrate for better interaction. Notably, human XPA is able to bind to the undamaged DNA duplex without any kinks, and XPA-DNA binding does not bend the DNA substrate obviously. This study provides structural basis for the binding mechanism of XPA to the undamaged splayed-arm DNA with a single pair of non-complementary nucleotides.
- Key Laboratory of Precision Oncology of Shandong Higher Education, Institute of Precision Medicine, Jining Medical University, Jining, Shandong 272067, China. Electronic address: fmlian@mail.jnmc.edu.cn.
Organizational Affiliation: