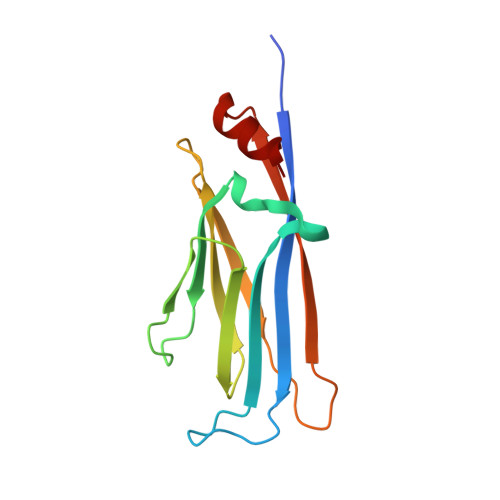
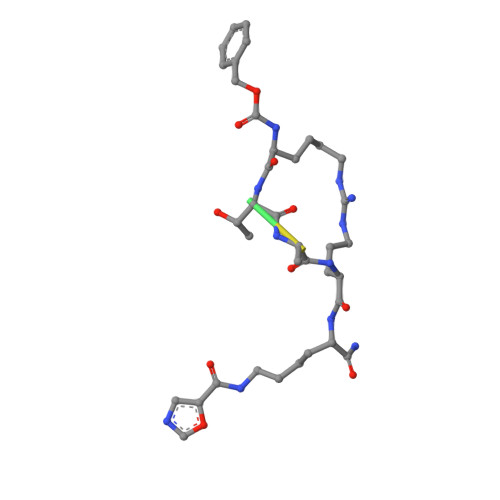
Selective Targeting of AF9 YEATS Domain by Cyclopeptide Inhibitors with Preorganized Conformation.
Jiang, Y., Chen, G., Li, X.M., Liu, S., Tian, G., Li, Y., Li, X., Li, H., Li, X.D.(2020) J Am Chem Soc 142: 21450-21459
- PubMed: 33306911
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c10324
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6L5Z - PubMed Abstract:
YEATS domains are newly identified epigenetic "readers" of histone lysine acetylation (Kac) and crotonylation (Kcr). The malfunction of YEATS-Kac/Kcr interactions has been found to be involved in the pathogenesis of human diseases, such as cancer. These discoveries suggest that the YEATS domains are promising novel drug targets. We and others recently reported the development of YEATS domain inhibitors. Although these inhibitors have a general preference toward the AF9 and ENL YEATS domains, selective inhibitors targeting either YEATS domain are challenging to develop as these two proteins share a high structural similarity. In this study, we identified a proximal site outside the acyllysine-binding pocket that can differentiate AF9 YEATS from ENL YEATS. Combinatorial targeting of both the acyllysine pocket and this additional site by conformationally preorganized cyclopeptides enabled the selective inhibition of the AF9 YEATS domain. The most selective inhibitor, JYX - 3 , showed a 38-fold higher binding affinity toward AF9 YEATS over ENL YEATS. Further investigations indicated that JYX - 3 could engage with AF9 in living cells, disrupt the YEATS-dependent chromatin recruitment of AF9, and suppress the transcription of AF9 target genes.
- Departments of Chemistry, The University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam Road, Hong Kong, China.
Organizational Affiliation: