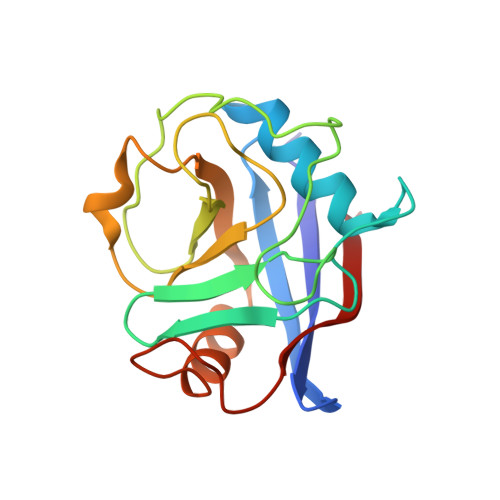
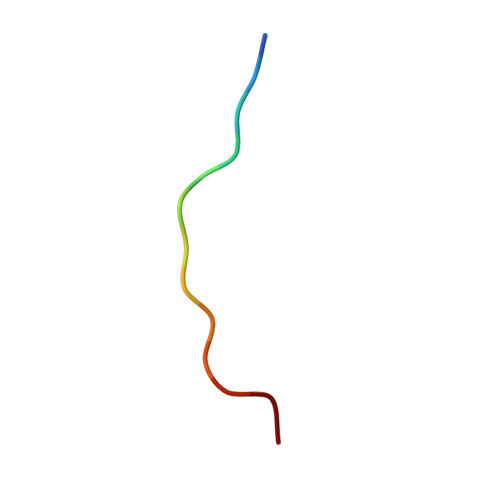The Molecular Basis of the Interaction of Cyclophilin A with alpha-Synuclein.
Favretto, F., Baker, J.D., Strohaker, T., Andreas, L.B., Blair, L.J., Becker, S., Zweckstetter, M.(2020) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 59: 5643-5646
- PubMed: 31830361
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201914878
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6I42 - PubMed Abstract:
Peptidylprolyl isomerases (PPIases) catalyze cis/trans isomerization of prolines. The PPIase CypA colocalizes with the Parkinson's disease (PD)-associated protein α-synuclein in cells and interacts with α-synuclein oligomers. Herein, we describe atomic insights into the molecular details of the α-synuclein/CypA interaction. NMR spectroscopy shows that CypA catalyzes isomerization of proline 128 in the C-terminal domain of α-synuclein. Strikingly, we reveal a second CypA-binding site formed by the hydrophobic sequence 47 GVVHGVATVA 56 , termed PreNAC. The 1.38 Å crystal structure of the CypA/PreNAC complex displays a contact between alanine 53 of α-synuclein and glutamine 111 in the catalytic pocket of CypA. Mutation of alanine 53 to glutamate, as found in patients with early-onset PD, weakens the interaction of α-synuclein with CypA. Our study provides high-resolution insights into the structure of the PD-associated protein α-synuclein in complex with the most abundant cellular cyclophilin.
- Translational Structural Biology in Dementia, German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE), Von-Siebold-Str. 3a, 37075, Göttingen, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: