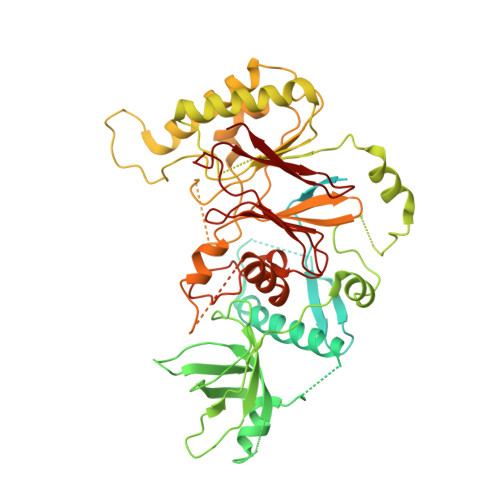
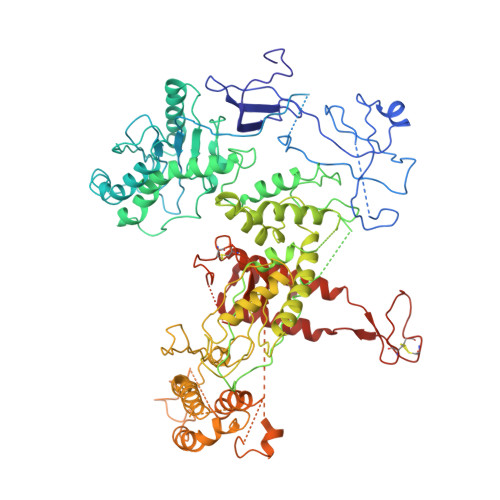
Structure of DNA-CMG-Pol epsilon elucidates the roles of the non-catalytic polymerase modules in the eukaryotic replisome.
Goswami, P., Abid Ali, F., Douglas, M.E., Locke, J., Purkiss, A., Janska, A., Eickhoff, P., Early, A., Nans, A., Cheung, A.M.C., Diffley, J.F.X., Costa, A.(2018) Nat Commun 9: 5061-5061
- PubMed: 30498216
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07417-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6HV8, 6HV9 - PubMed Abstract:
Eukaryotic origin firing depends on assembly of the Cdc45-MCM-GINS (CMG) helicase. A key step is the recruitment of GINS that requires the leading-strand polymerase Pol epsilon, composed of Pol2, Dpb2, Dpb3, Dpb4. While a truncation of the catalytic N-terminal Pol2 supports cell division, Dpb2 and C-terminal Pol2 (C-Pol2) are essential for viability. Dpb2 and C-Pol2 are non-catalytic modules, shown or predicted to be related to an exonuclease and DNA polymerase, respectively. Here, we present the cryo-EM structure of the isolated C-Pol2/Dpb2 heterodimer, revealing that C-Pol2 contains a DNA polymerase fold. We also present the structure of CMG/C-Pol2/Dpb2 on a DNA fork, and find that polymerase binding changes both the helicase structure and fork-junction engagement. Inter-subunit contacts that keep the helicase-polymerase complex together explain several cellular phenotypes. At least some of these contacts are preserved during Pol epsilon-dependent CMG assembly on path to origin firing, as observed with DNA replication reconstituted in vitro.
- Macromolecular Machines Laboratory, The Francis Crick Institute, 1 Midland Road, London, NW1 1AT, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: