Insights into Urease Inhibition by N-( n-Butyl) Phosphoric Triamide through an Integrated Structural and Kinetic Approach.
Mazzei, L., Cianci, M., Contaldo, U., Ciurli, S.(2019) J Agric Food Chem 67: 2127-2138
- PubMed: 30735374
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b04791
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6H8J - PubMed Abstract:
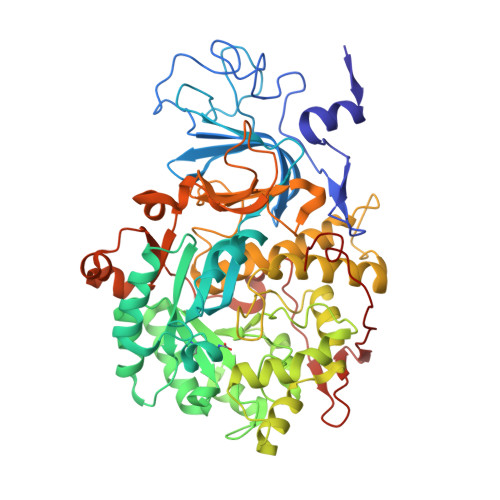
The nickel-dependent enzyme urease represents a negative element for the efficiency of soil nitrogen fertilization as well as a virulence factor for a large number of pathogenic and antibiotic-resistant bacteria. The development of ever more efficient urease inhibitors demands knowledge of their modes of action at the molecular level. N-( n-Butyl)-phosphoric triamide (NBPTO) is the oxo-derivative of N-( n-butyl)-thiophosphoric triamide (NBPT), which is extensively employed in agriculture to increase the efficiency of urea-based fertilizers. The 1.45 Å resolution structure of the enzyme-inhibitor complex obtained upon incubation of Sporosarcina pasteurii urease (SPU) with NBPTO shows the presence of diamido phosphoric acid (DAP), generated upon enzymatic hydrolysis of NBPTO with the release of n-butyl amine. DAP is bound in a tridentate binding mode to the two Ni(II) ions in the active site of urease via two O atoms and an amide NH 2 group, whereas the second amide group of DAP points away from the metal center into the active-site channel. The mobile flap modulating the size of the active-site cavity is found in a disordered closed-open conformation. A kinetic characterization of the NBPTO-based inhibition of both bacterial (SPU) and plant ( Canavalia ensiformis or jack bean, JBU) ureases, carried out by calorimetric measurements, indicates the occurrence of a reversible slow-inhibition mode of action. The latter is characterized by a very small value of the equilibrium dissociation constant of the urease-DAP complex caused, in turn, by the large rate constant for the formation of the enzyme-inhibitor complex. The much greater capability of NBPTO to inhibit urease, as compared with that of NBPT, is thus not caused by the presence of a P═O moiety versus a P═S moiety, as previously suggested, but rather by the readiness of NBPTO to react with urease without the need to convert one of the P-NH 2 amide moieties to its P-OH acid derivative, as in the case of NBPT. The latter process is indeed characterized by a very small equilibrium constant that reduces drastically the concentration of the active form of the inhibitor in the case of NBPT. This indicates that high-efficiency phosphoramide-based urease inhibitors must have at least one O atom bound to the central P atom in order for the molecule to efficiently and rapidly bind to the dinickel center of the enzyme.
- Laboratory of Bioinorganic Chemistry, Department of Pharmacy and Biotechnology , University of Bologna , 40126 Bologna , Italy.
Organizational Affiliation: