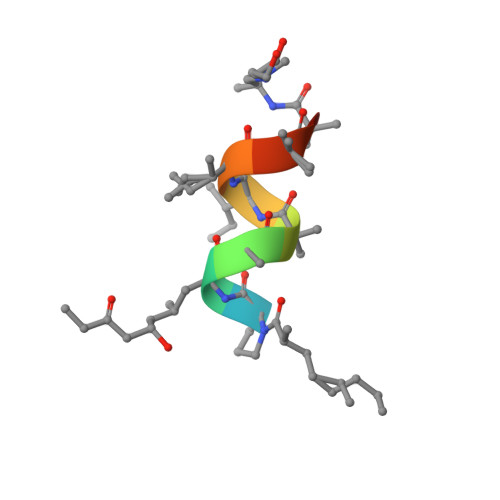
Aminolipopeptide helioferin A and B
Gessmann, R., Petratos, K.(2018) Acta Cryst D 74
- PubMed: 29652258
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798318001857
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6EVH - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of the natural nonapeptide antibiotic helioferin has been determined and refined to 0.9 Å resolution. Helioferin consists of helioferin A and B, which contain 2-(2'-aminopropyl)aminoethanol (Apae) and 2-[(2'-aminopropyl)methylamino]ethanol (Amae) at their respective alkanolamine termini. In addition, helioferin contains the unusual amino-acid residues α-aminoisobutyric acid (Aib) and (2S,4S,6S)-2-amino-6-hydroxy-4-methyl-8-oxodecanoic acid (Ahmod). The amino-terminus is capped with 2-methyl-n-1-octanoic acid (M8a). The peptide crystallizes with a 1:1 molar ratio of helioferin A and B in the monoclinic space group C2, with unit-cell parameters a = 34.711, b = 10.886, c = 17.150 Å, β = 93.05°. The peptide backbone folds in a regular right-handed α-helical conformation, with eight intramolecular hydrogen bonds, all but one forming 5→1 interactions. The two aliphatic chains of the fatty-acyl (M8a) and the second residue (Ahmod) extend out of the α-helical structure in opposite directions and lead to a corkscrew-like shape of the peptide molecule. Halogen anions (Cl - and F - ) have been co-crystallized with the peptide molecules, implying a positive charge at the aminoalcohol end of the peptide. In the tightly packed crystal the helices are linked head to tail via the anions by electrostatic, hydrogen-bond and van der Waals interactions, forming continuous helical rods. Two nonparallel rods (forming an angle of 118°) interact directly via hydrogen bonds and via the anions, forming a double layer. Successive double layers are held together only via van der Waals contacts. The helical axes of successive double layers are also related by an angle of 118°. The structure of helioferin reported here and the previously determined structure of the homologous leucinostatin A have a total straight length of about 21 Å, indicating a different membrane-modifying bioactivity from that of long-chain, amphiphilic peptaibols.
- IMBB-FORTH, N. Plastira 100, 70013 Heraklion, Greece.
Organizational Affiliation: