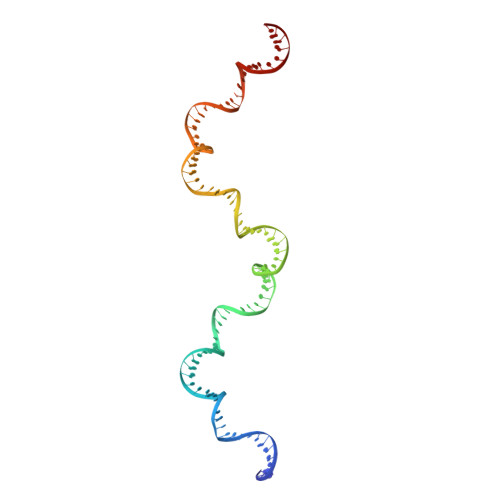
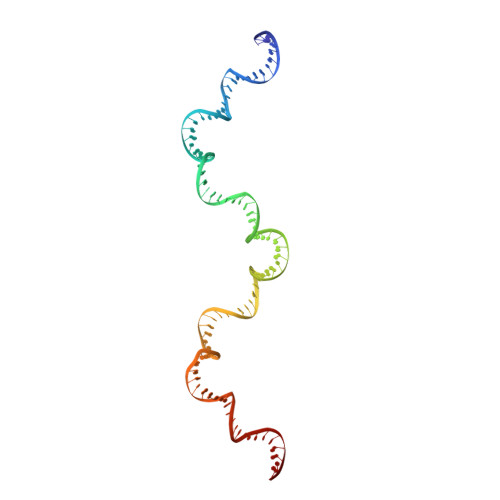
The MerR-like protein BldC binds DNA direct repeats as cooperative multimers to regulate Streptomyces development.
Schumacher, M.A., den Hengst, C.D., Bush, M.J., Le, T.B.K., Tran, N.T., Chandra, G., Zeng, W., Travis, B., Brennan, R.G., Buttner, M.J.(2018) Nat Commun 9: 1139-1139
- PubMed: 29556010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03576-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6AMA, 6AMK - PubMed Abstract:
Streptomycetes are notable for their complex life cycle and production of most clinically important antibiotics. A key factor that controls entry into development and the onset of antibiotic production is the 68-residue protein, BldC. BldC is a putative DNA-binding protein related to MerR regulators, but lacks coiled-coil dimerization and effector-binding domains characteristic of classical MerR proteins. Hence, the molecular function of the protein has been unclear. Here we show that BldC is indeed a DNA-binding protein and controls a regulon that includes other key developmental regulators. Intriguingly, BldC DNA-binding sites vary significantly in length. Our BldC-DNA structures explain this DNA-binding capability by revealing that BldC utilizes a DNA-binding mode distinct from MerR and other known regulators, involving asymmetric head-to-tail oligomerization on DNA direct repeats that results in dramatic DNA distortion. Notably, BldC-like proteins radiate throughout eubacteria, establishing BldC as the founding member of a new structural family of regulators.
- Department of Biochemistry, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, NC, 27710, USA. maria.schumacher@duke.edu.
Organizational Affiliation: