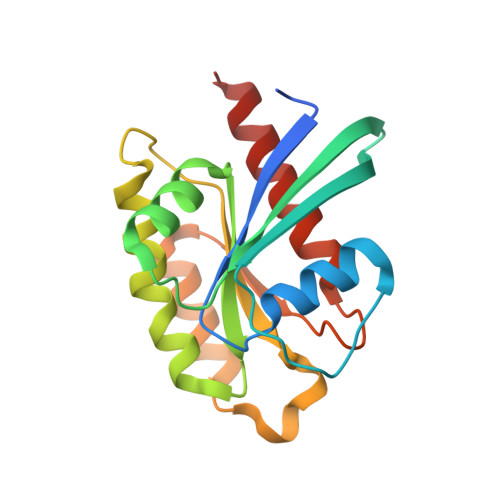
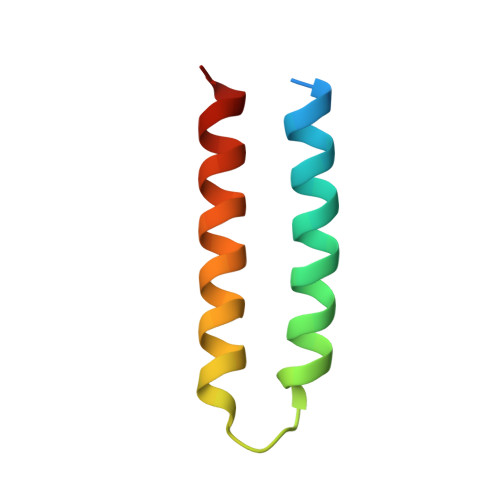
Affinity maturation of the RLIP76 Ral binding domain to inform the design of stapled peptides targeting the Ral GTPases.
Hurd, C.A., Brear, P., Revell, J., Ross, S., Mott, H.R., Owen, D.(2020) J Biological Chem 296: 100101-100101
- PubMed: 33214225
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.015735
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6ZQT, 6ZRN - PubMed Abstract:
Ral GTPases have been implicated as critical drivers of cell growth and metastasis in numerous Ras-driven cancers. We have previously reported stapled peptides, based on the Ral effector RLIP76, that can disrupt Ral signaling. Stapled peptides are short peptides that are locked into their bioactive form using a synthetic brace. Here, using an affinity maturation of the RLIP76 Ral-binding domain, we identified several sequence substitutions that together improve binding to Ral proteins by more than 20-fold. Hits from the selection were rigorously analyzed to determine the contributions of individual residues and two 1.5 Å cocrystal structures of the tightest-binding mutants in complex with RalB revealed key interactions. Insights gained from this maturation were used to design second-generation stapled peptides based on RLIP76 that exhibited vastly improved selectivity for Ral GTPases when compared with the first-generation lead peptide. The binding of second-generation peptides to Ral proteins was quantified and the binding site of the lead peptide on RalB was determined by NMR. Stapled peptides successfully competed with multiple Ral-effector interactions in cellular lysates. Our findings demonstrate how manipulation of a native binding partner can assist in the rational design of stapled peptide inhibitors targeting a protein-protein interaction.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: