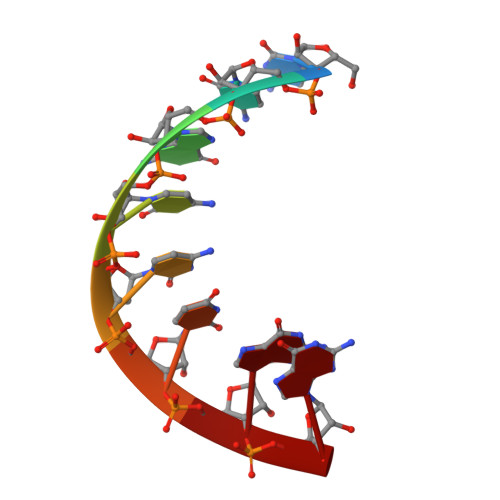
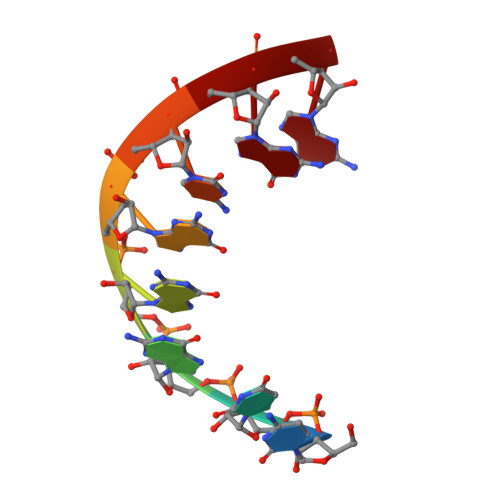
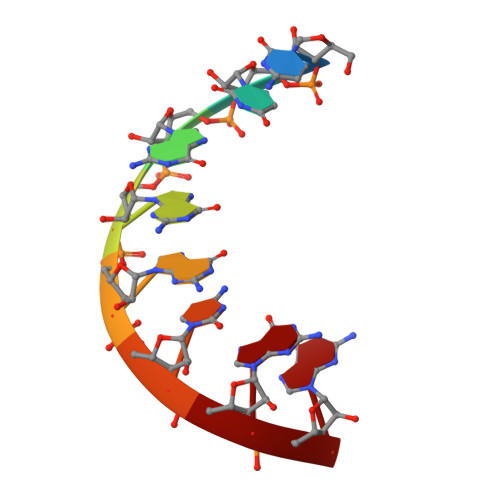
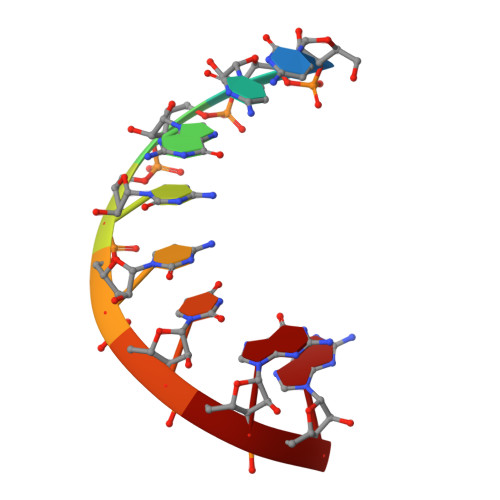
Broken symmetry between RNA enantiomers in a crystal lattice.
Kiliszek, A., Blaszczyk, L., Bejger, M., Rypniewski, W.(2021) Nucleic Acids Res 49: 12535-12539
- PubMed: 34107036
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab480
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6ZPF, 6ZQ9, 6ZR1, 6ZRL, 6ZRS, 6ZW3, 6ZWU, 6ZX5, 6ZX8, 7A9L, 7A9N, 7A9O, 7A9P, 7A9Q, 7A9R, 7A9S, 7A9T - PubMed Abstract:
Explaining the origin of the homochirality of biological molecules requires a mechanism of disrupting the natural equilibrium between enantiomers and amplifying the initial imbalance to significant levels. Authors of existing models have sought an explanation in the parity-breaking weak nuclear force, in some selectively acting external factor, or in random fluctuations that subsequently became amplified by an autocatalytic process. We have obtained crystals in which l- and d-enantiomers of short RNA duplexes assemble in an asymmetric manner. These enantiomers make different lattice contacts and have different exposures to water and metal ions present in the crystal. Apparently, asymmetry between enantiomers can arise upon their mutual interactions and then propagate via crystallization. Asymmetric racemic compounds are worth considering as possible factors in symmetry breaking and enantioenrichment that took place in the early biosphere.
- Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, Polish Academy of Sciences, Noskowskiego 12/14, 61-704 Poznań, Poland.
Organizational Affiliation: