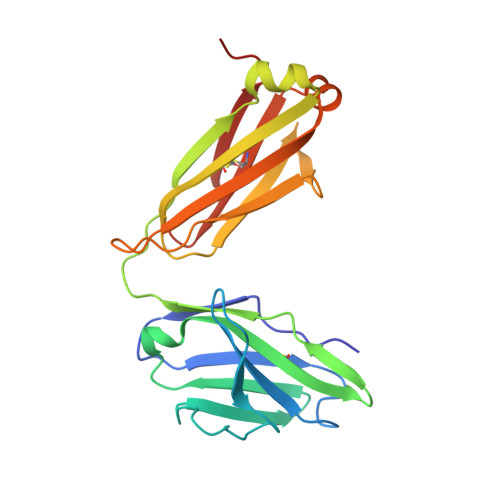
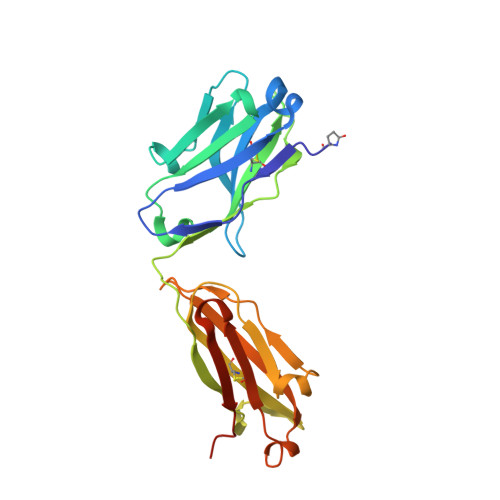
Affinity maturation is required for pathogenic monovalent IgG4 autoantibody development in myasthenia gravis.
Fichtner, M.L., Vieni, C., Redler, R.L., Kolich, L., Jiang, R., Takata, K., Stathopoulos, P., Suarez, P.A., Nowak, R.J., Burden, S.J., Ekiert, D.C., O'Connor, K.C.(2020) J Exp Medicine 217
- PubMed: 32820331
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20200513
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6WYR, 6WYT - PubMed Abstract:
Pathogenic muscle-specific tyrosine kinase (MuSK)-specific IgG4 autoantibodies in autoimmune myasthenia gravis (MG) are functionally monovalent as a result of Fab-arm exchange. The development of these unique autoantibodies is not well understood. We examined MG patient-derived monoclonal autoantibodies (mAbs), their corresponding germline-encoded unmutated common ancestors (UCAs), and monovalent antigen-binding fragments (Fabs) to investigate how affinity maturation contributes to binding and immunopathology. Mature mAbs, UCA mAbs, and mature monovalent Fabs bound to MuSK and demonstrated pathogenic capacity. However, monovalent UCA Fabs bound to MuSK but did not have measurable pathogenic capacity. Affinity of the UCA Fabs for MuSK was 100-fold lower than the subnanomolar affinity of the mature Fabs. Crystal structures of two Fabs revealed how mutations acquired during affinity maturation may contribute to increased MuSK-binding affinity. These findings indicate that the autoantigen drives autoimmunity in MuSK MG through the accumulation of somatic mutations such that monovalent IgG4 Fab-arm-exchanged autoantibodies reach a high-affinity threshold required for pathogenic capacity.
- Department of Neurology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT.
Organizational Affiliation: