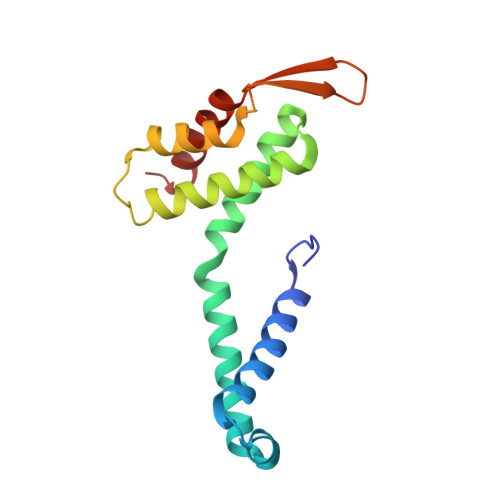
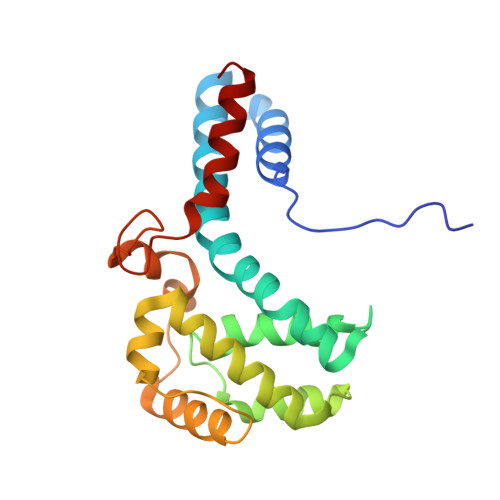
Structures of filamentous viruses infecting hyperthermophilic archaea explain DNA stabilization in extreme environments.
Wang, F., Baquero, D.P., Beltran, L.C., Su, Z., Osinski, T., Zheng, W., Prangishvili, D., Krupovic, M., Egelman, E.H.(2020) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117: 19643-19652
- PubMed: 32759221
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2011125117
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6WQ0, 6WQ2 - PubMed Abstract:
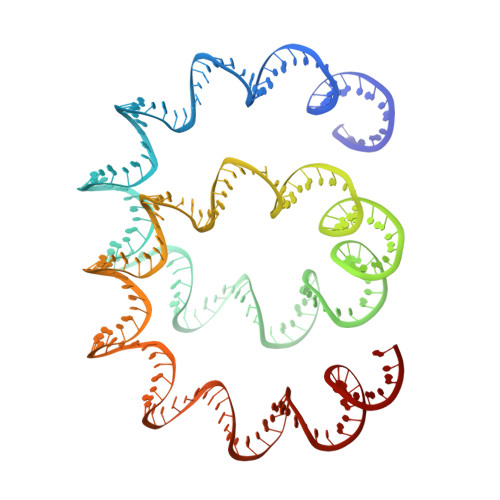
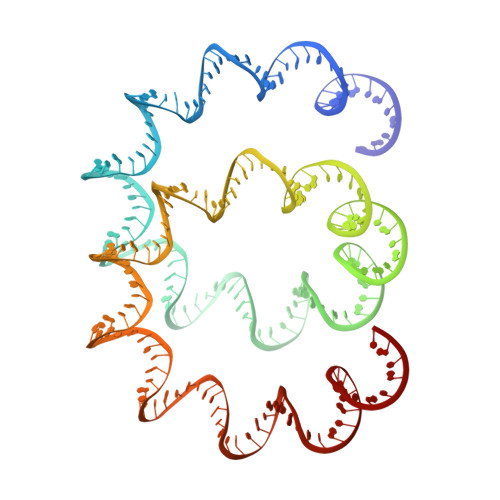
Living organisms expend metabolic energy to repair and maintain their genomes, while viruses protect their genetic material by completely passive means. We have used cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to solve the atomic structures of two filamentous double-stranded DNA viruses that infect archaeal hosts living in nearly boiling acid: Saccharolobus solfataricus rod-shaped virus 1 (SSRV1), at 2.8-Å resolution, and Sulfolobus islandicus filamentous virus (SIFV), at 4.0-Å resolution. The SIFV nucleocapsid is formed by a heterodimer of two homologous proteins and is membrane enveloped, while SSRV1 has a nucleocapsid formed by a homodimer and is not enveloped. In both, the capsid proteins wrap around the DNA and maintain it in an A-form. We suggest that the A-form is due to both a nonspecific desolvation of the DNA by the protein, and a specific coordination of the DNA phosphate groups by positively charged residues. We extend these observations by comparisons with four other archaeal filamentous viruses whose structures we have previously determined, and show that all 10 capsid proteins (from four heterodimers and two homodimers) have obvious structural homology while sequence similarity can be nonexistent. This arises from most capsid residues not being under any strong selective pressure. The inability to detect homology at the sequence level arises from the sampling of viruses in this part of the biosphere being extremely sparse. Comparative structural and genomic analyses suggest that nonenveloped archaeal viruses have evolved from enveloped viruses by shedding the membrane, indicating that this trait may be relatively easily lost during virus evolution.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA 22908.
Organizational Affiliation: