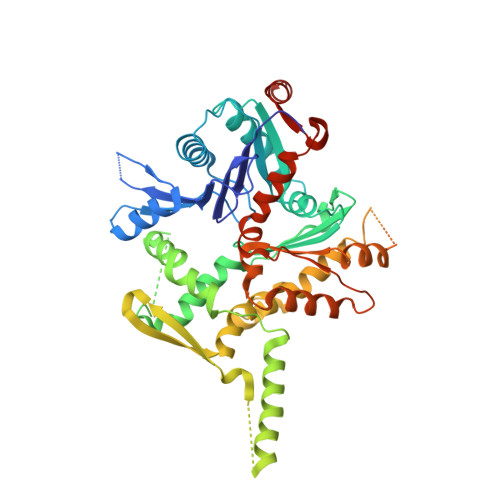
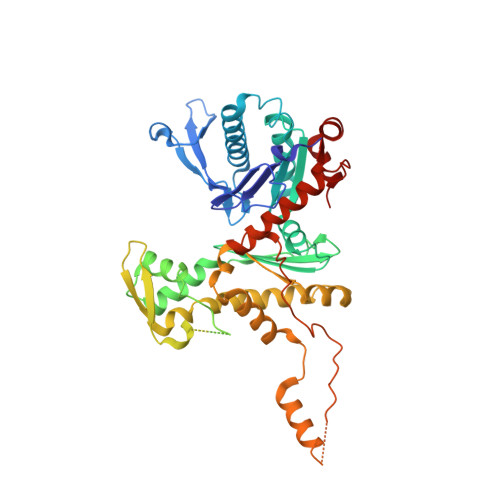
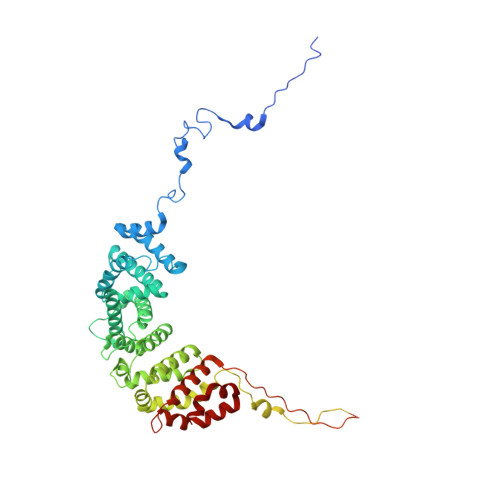
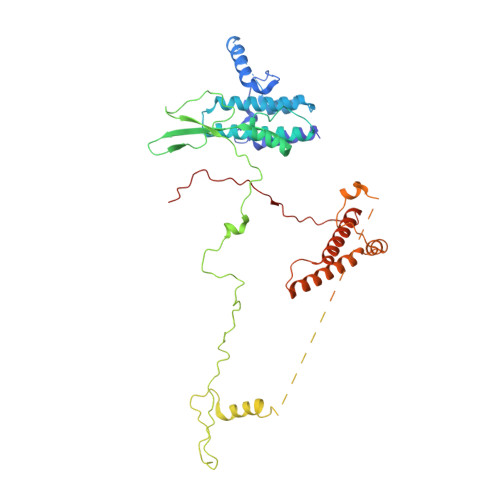
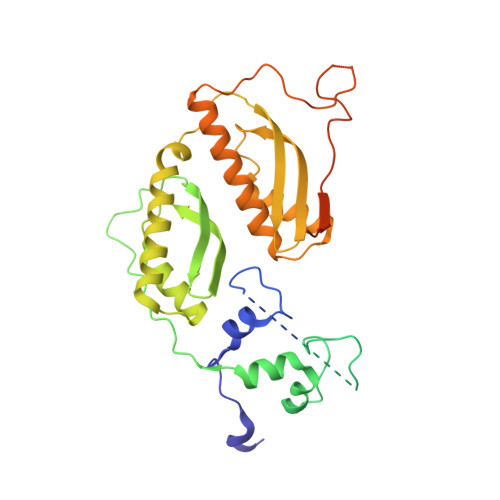
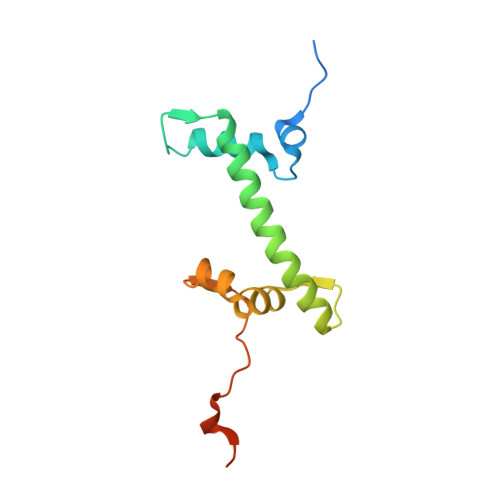
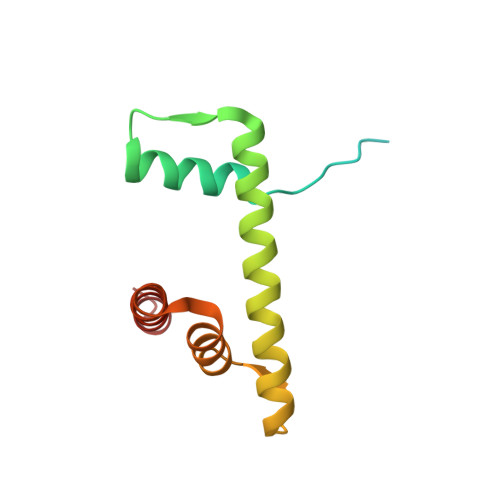
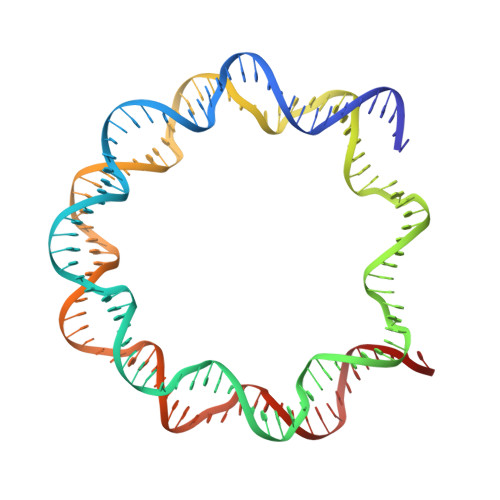
Architecture of the chromatin remodeler RSC and insights into its nucleosome engagement.
Patel, A.B., Moore, C.M., Greber, B.J., Luo, J., Zukin, S.A., Ranish, J., Nogales, E.(2019) Elife 8
- PubMed: 31886770
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.54449
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6V8O, 6V92 - PubMed Abstract:
Eukaryotic DNA is packaged into nucleosome arrays, which are repositioned by chromatin remodeling complexes to control DNA accessibility. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae RSC ( R emodeling the S tructure of C hromatin) complex, a member of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeler family, plays critical roles in genome maintenance, transcription, and DNA repair. Here, we report cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and crosslinking mass spectrometry (CLMS) studies of yeast RSC complex and show that RSC is composed of a rigid tripartite core and two flexible lobes. The core structure is scaffolded by an asymmetric Rsc8 dimer and built with the evolutionarily conserved subunits Sfh1, Rsc6, Rsc9 and Sth1. The flexible ATPase lobe, composed of helicase subunit Sth1, Arp7, Arp9 and Rtt102, is anchored to this core by the N-terminus of Sth1. Our cryo-EM analysis of RSC bound to a nucleosome core particle shows that in addition to the expected nucleosome-Sth1 interactions, RSC engages histones and nucleosomal DNA through one arm of the core structure, composed of the Rsc8 SWIRM domains, Sfh1 and Npl6. Our findings provide structural insights into the conserved assembly process for all members of the SWI/SNF family of remodelers, and illustrate how RSC selects, engages, and remodels nucleosomes.
- Biophysics Graduate Group, University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: