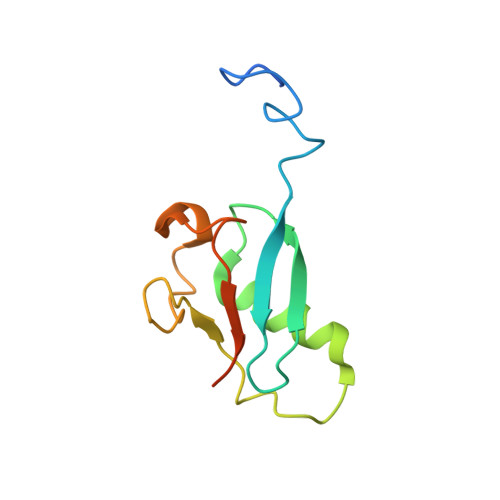
Structural Basis of Paxillin Recruitment by Kindlin-2 in Regulating Cell Adhesion.
Zhu, L., Liu, H., Lu, F., Yang, J., Byzova, T.V., Qin, J.(2019) Structure 27: 1686
- PubMed: 31590942
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2019.09.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6U4M, 6U4N - PubMed Abstract:
Activation of cell surface receptor integrin has been extensively studied as the first key step to trigger cell adhesion, but the subsequent events, widely regarded as integrin "outside-in" signaling to form supramolecular complexes (focal adhesions [FAs]) to promote dynamic cell adhesion, remain poorly elucidated. Integrin activator kindlin-2 was recently found to associate with paxillin in nascent FAs, implicating an early yet undefined integrin outside-in signaling event. Here we show structurally that kindlin-2 recognizes paxillin via a distinct interface involving the ubiquitin-like kindlin-2 F0 domain and the paxillin LIM4 domain. The interface is adjacent to the membrane binding site of kindlin-2 F0, suggesting a mechanism for kindlin-2 to recruit paxillin to the membrane-proximal site where FA assembly is initiated. Disruption of the interface impaired the localization of paxillin, causing strong defects in FA assembly and cell migration. These data unveil a structural basis of the kindlin-2/paxillin interaction in controlling dynamic cell adhesion.
- Department of Cardiovascular & Metabolic Sciences, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, 9500 Euclid Avenue, Cleveland, OH 44195, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: