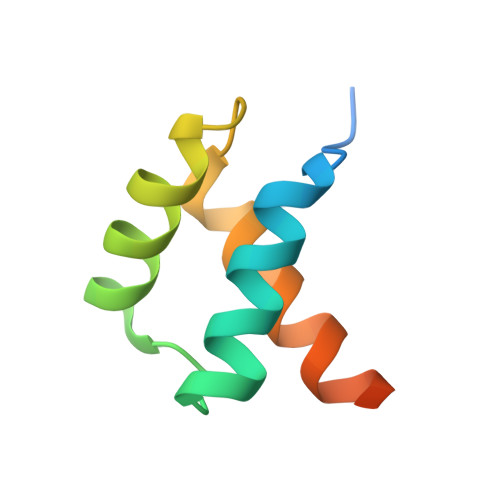
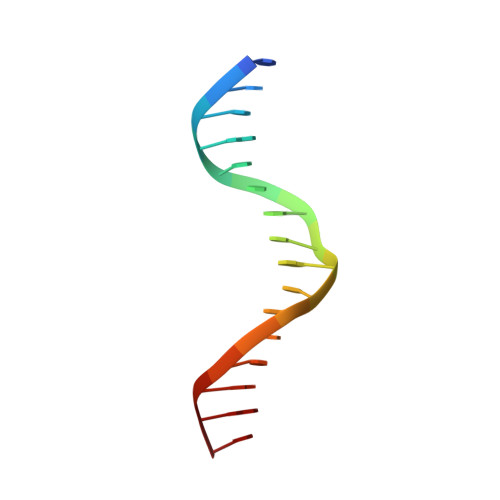
Structural basis for the complex DNA binding behavior of the plant stem cell regulator WUSCHEL.
Sloan, J., Hakenjos, J.P., Gebert, M., Ermakova, O., Gumiero, A., Stier, G., Wild, K., Sinning, I., Lohmann, J.U.(2020) Nat Commun 11: 2223-2223
- PubMed: 32376862
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16024-y
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6RY3, 6RYD, 6RYI, 6RYL - PubMed Abstract:
Stem cells are one of the foundational evolutionary novelties that allowed the independent emergence of multicellularity in the plant and animal lineages. In plants, the homeodomain (HD) transcription factor WUSCHEL (WUS) is essential for the maintenance of stem cells in the shoot apical meristem. WUS has been reported to bind to diverse DNA motifs and to act as transcriptional activator and repressor. However, the mechanisms underlying this remarkable behavior have remained unclear. Here, we quantitatively delineate WUS binding to three divergent DNA motifs and resolve the relevant structural underpinnings. We show that WUS exhibits a strong binding preference for TGAA repeat sequences, while retaining the ability to weakly bind to TAAT elements. This behavior is attributable to the formation of dimers through interactions of specific residues in the HD that stabilize WUS DNA interaction. Our results provide a mechanistic basis for dissecting WUS dependent regulatory networks in plant stem cell control.
- Biochemistry Center, Heidelberg University, Im Neuenheimer Feld 328, 69120, Heidelberg, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: