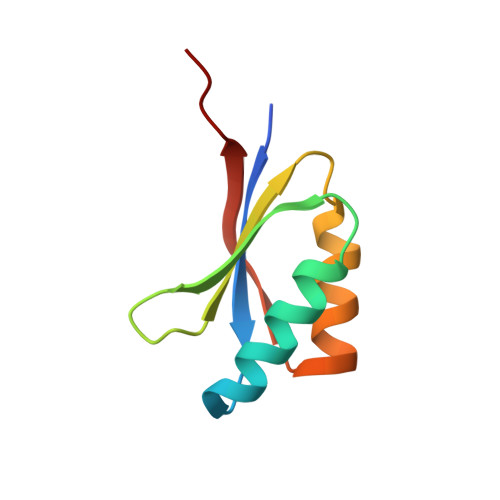
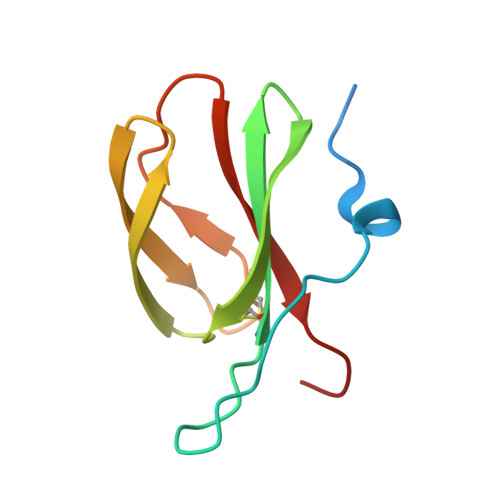
Protein engineering expands the effector recognition profile of a rice NLR immune receptor.
De la Concepcion, J.C., Franceschetti, M., MacLean, D., Terauchi, R., Kamoun, S., Banfield, M.J.(2019) Elife 8
- PubMed: 31535976
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47713
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6R8K, 6R8M - PubMed Abstract:
Plant nucleotide binding, leucine-rich repeat (NLR) receptors detect pathogen effectors and initiate an immune response. Since their discovery, NLRs have been the focus of protein engineering to improve disease resistance. However, this approach has proven challenging, in part due to their narrow response specificity. Previously, we revealed the structural basis of pathogen recognition by the integrated heavy metal associated (HMA) domain of the rice NLR Pikp (Maqbool et al., 2015). Here, we used structure-guided engineering to expand the response profile of Pikp to variants of the rice blast pathogen effector AVR-Pik. A mutation located within an effector-binding interface of the integrated Pikp-HMA domain increased the binding affinity for AVR-Pik variants in vitro and in vivo. This translates to an expanded cell-death response to AVR-Pik variants previously unrecognized by Pikp in planta. The structures of the engineered Pikp-HMA in complex with AVR-Pik variants revealed the mechanism of expanded recognition. These results provide a proof-of-concept that protein engineering can improve the utility of plant NLR receptors where direct interaction between effectors and NLRs is established, particularly where this interaction occurs via integrated domains.
- Department of Biological Chemistry, John Innes Centre, Norwich, United Kingdom.
Organizational Affiliation: