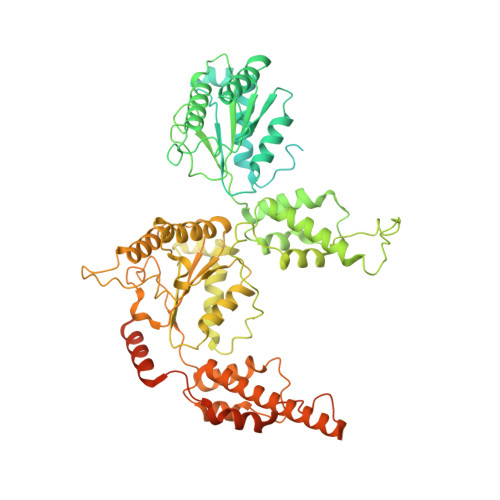
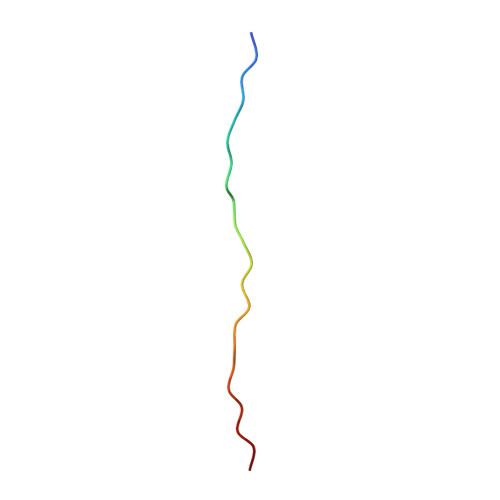Structure of the Cdc48 segregase in the act of unfolding an authentic substrate.
Cooney, I., Han, H., Stewart, M.G., Carson, R.H., Hansen, D.T., Iwasa, J.H., Price, J.C., Hill, C.P., Shen, P.S.(2019) Science 365: 502-505
- PubMed: 31249134
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aax0486
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6OMB, 6OPC - PubMed Abstract:
The cellular machine Cdc48 functions in multiple biological pathways by segregating its protein substrates from a variety of stable environments such as organelles or multi-subunit complexes. Despite extensive studies, the mechanism of Cdc48 has remained obscure, and its reported structures are inconsistent with models of substrate translocation proposed for other AAA+ ATPases (adenosine triphosphatases). Here, we report a 3.7-angstrom-resolution structure of Cdc48 in complex with an adaptor protein and a native substrate. Cdc48 engages substrate by adopting a helical configuration of substrate-binding residues that extends through the central pore of both of the ATPase rings. These findings indicate a unified hand-over-hand mechanism of protein translocation by Cdc48 and other AAA+ ATPases.
- Department of Biochemistry, 15 N. Medical Drive East, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT 84112, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: