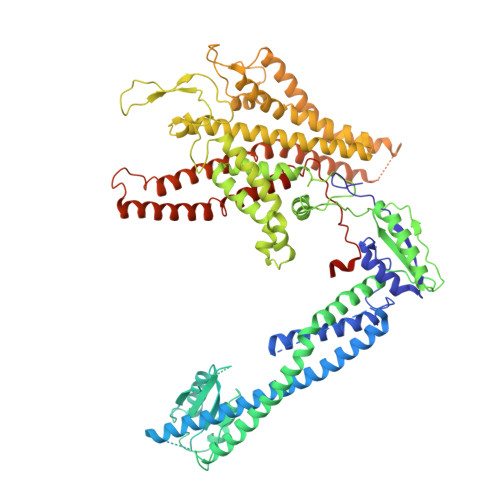
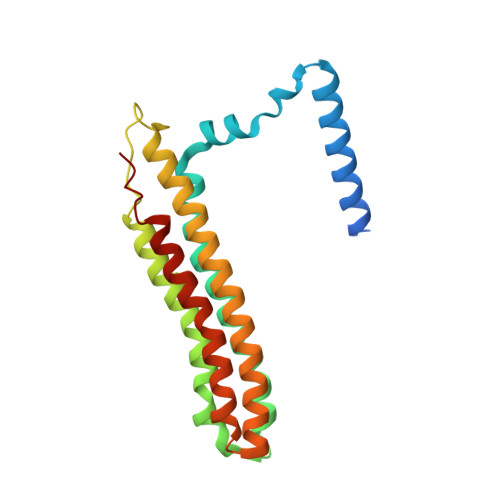
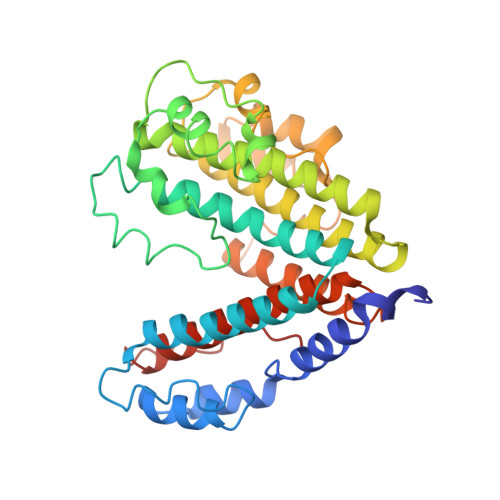
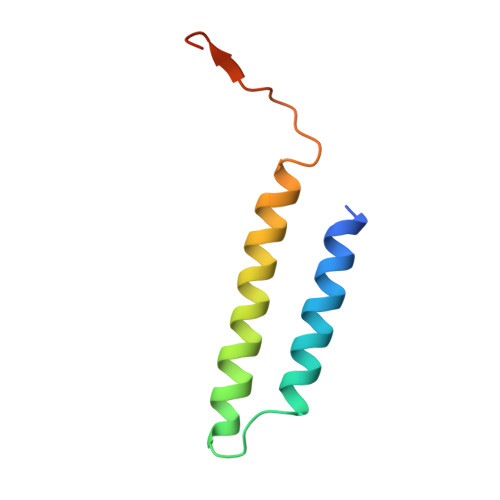
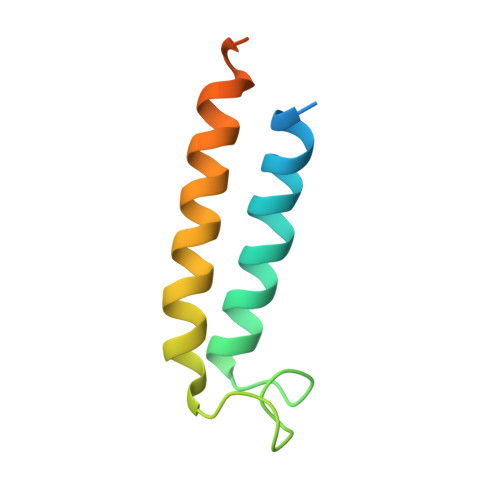
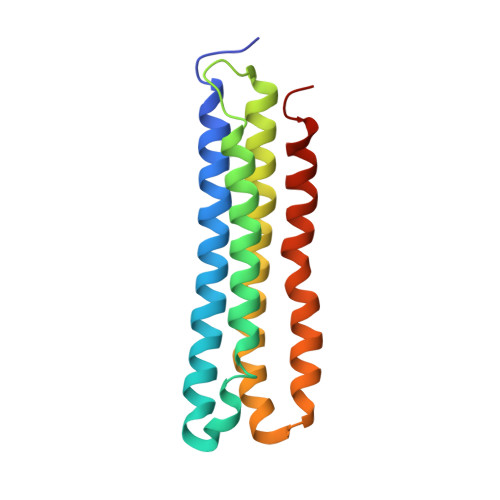
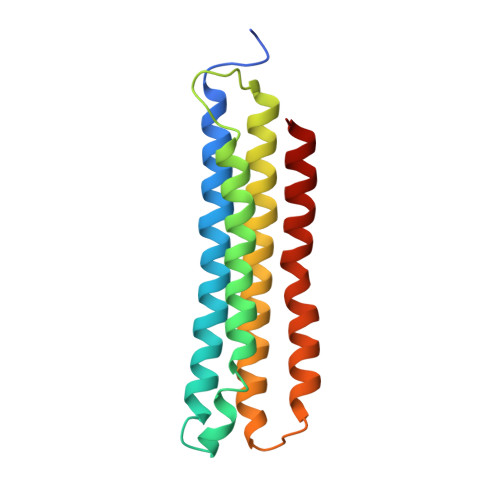
Structural comparison of the vacuolar and Golgi V-ATPases fromSaccharomyces cerevisiae.
Vasanthakumar, T., Bueler, S.A., Wu, D., Beilsten-Edmands, V., Robinson, C.V., Rubinstein, J.L.(2019) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116: 7272-7277
- PubMed: 30910982
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1814818116
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6O7T, 6O7U, 6O7V, 6O7W, 6O7X - PubMed Abstract:
Proton-translocating vacuolar-type ATPases (V-ATPases) are necessary for numerous processes in eukaryotic cells, including receptor-mediated endocytosis, protein maturation, and lysosomal acidification. In mammals, V-ATPase subunit isoforms are differentially targeted to various intracellular compartments or tissues, but how these subunit isoforms influence enzyme activity is not clear. In the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae , isoform diversity is limited to two different versions of the proton-translocating subunit a: Vph1p, which is targeted to the vacuole, and Stv1p, which is targeted to the Golgi apparatus and endosomes. We show that purified V-ATPase complexes containing Vph1p have higher ATPase activity than complexes containing Stv1p and that the relative difference in activity depends on the presence of lipids. We also show that V O complexes containing Stv1p could be readily purified without attached V 1 regions. We used this effect to determine structures of the membrane-embedded V O region with Stv1p at 3.1-Å resolution, which we compare with a structure of the V O region with Vph1p that we determine to 3.2-Å resolution. These maps reveal differences in the surface charge near the cytoplasmic proton half-channel. Both maps also show the presence of bound lipids, as well as regularly spaced densities that may correspond to ergosterol or bound detergent, around the c-ring.
- Molecular Medicine Program, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, ON M5G 0A4, Canada.
Organizational Affiliation: