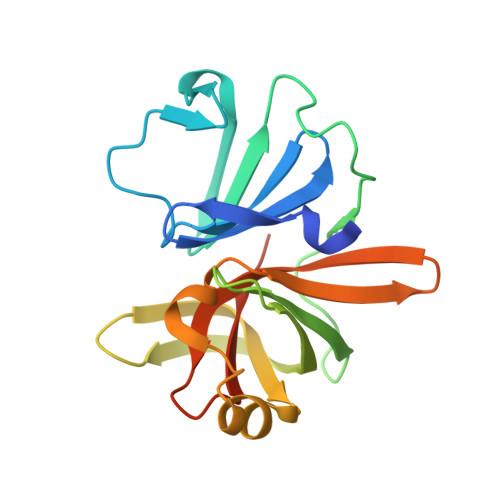
GII.4 Norovirus Protease Shows pH-Sensitive Proteolysis with a Unique Arg-His Pairing in the Catalytic Site.
Viskovska, M.A., Zhao, B., Shanker, S., Choi, J.M., Deng, L., Song, Y., Palzkill, T., Hu, L., Estes, M.K., Venkataram Prasad, B.V.(2019) J Virol 93
- PubMed: 30626675
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01479-18
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6NIR - PubMed Abstract:
Human noroviruses (NoVs) are the main cause of epidemic and sporadic gastroenteritis. Phylogenetically, noroviruses are divided into seven genogroups, with each divided into multiple genotypes. NoVs belonging to genogroup II and genotype 4 (GII.4) are globally most prevalent. Genetic diversity among the NoVs and the periodic emergence of novel strains present a challenge for the development of vaccines and antivirals to treat NoV infection. NoV protease is essential for viral replication and is an attractive target for the development of antivirals. The available structure of GI.1 protease provided a basis for the design of inhibitors targeting the active site of the protease. These inhibitors, although potent against the GI proteases, poorly inhibit the GII proteases, for which structural information is lacking. To elucidate the structural basis for this difference in the inhibitor efficiency, we determined the crystal structure of a GII.4 protease. The structure revealed significant changes in the S2 substrate-binding pocket, making it noticeably smaller, and in the active site, with the catalytic triad residues showing conformational changes. Furthermore, a conserved arginine is found inserted into the active site, interacting with the catalytic histidine and restricting substrate/inhibitor access to the S2 pocket. This interaction alters the relationships between the catalytic residues and may allow for a pH-dependent regulation of protease activity. The changes we observed in the GII.4 protease structure may explain the reduced potency of the GI-specific inhibitors against the GII protease and therefore must be taken into account when designing broadly cross-reactive antivirals against NoVs. IMPORTANCE Human noroviruses (NoVs) cause sporadic and epidemic gastroenteritis worldwide. They are divided into seven genogroups (GI to GVII), with each genogroup further divided into several genotypes. Human NoVs belonging to genogroup II and genotype 4 (GII.4) are the most prevalent. Currently, there are no vaccines or antiviral drugs available for NoV infection. The protease encoded by NoV is considered a valuable target because of its essential role in replication. NoV protease structures have only been determined for the GI genogroup. We show here that the structure of the GII.4 protease exhibits several significant changes from GI proteases, including a unique pairing of an arginine with the catalytic histidine that makes the proteolytic activity of GII.4 protease pH sensitive. A comparative analysis of NoV protease structures may provide a rational framework for structure-based drug design of broadly cross-reactive inhibitors targeting NoVs.
- The Verna and Marrs McLean Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: