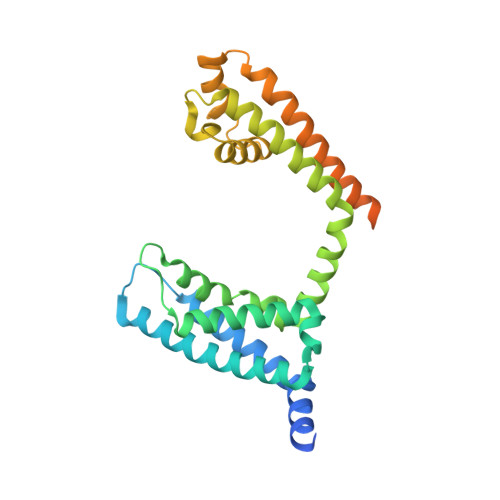
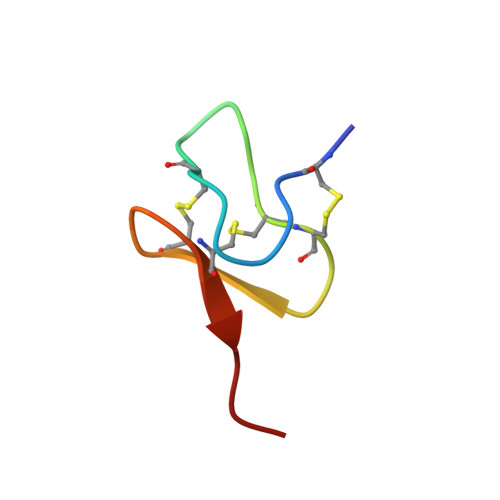
Structural Basis of Nav1.7 Inhibition by a Gating-Modifier Spider Toxin.
Xu, H., Li, T., Rohou, A., Arthur, C.P., Tzakoniati, F., Wong, E., Estevez, A., Kugel, C., Franke, Y., Chen, J., Ciferri, C., Hackos, D.H., Koth, C.M., Payandeh, J.(2019) Cell 176: 702-715.e14
- PubMed: 30661758
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.12.018
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6N4I, 6N4Q, 6N4R - PubMed Abstract:
Voltage-gated sodium (Nav) channels are targets of disease mutations, toxins, and therapeutic drugs. Despite recent advances, the structural basis of voltage sensing, electromechanical coupling, and toxin modulation remains ill-defined. Protoxin-II (ProTx2) from the Peruvian green velvet tarantula is an inhibitor cystine-knot peptide and selective antagonist of the human Nav1.7 channel. Here, we visualize ProTx2 in complex with voltage-sensor domain II (VSD2) from Nav1.7 using X-ray crystallography and cryoelectron microscopy. Membrane partitioning orients ProTx2 for unfettered access to VSD2, where ProTx2 interrogates distinct features of the Nav1.7 receptor site. ProTx2 positions two basic residues into the extracellular vestibule to antagonize S4 gating-charge movement through an electrostatic mechanism. ProTx2 has trapped activated and deactivated states of VSD2, revealing a remarkable ∼10 Å translation of the S4 helix, providing a structural framework for activation gating in voltage-gated ion channels. Finally, our results deliver key templates to design selective Nav channel antagonists.
- Department of Structural Biology, Genentech, South San Francisco, CA 94080, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: