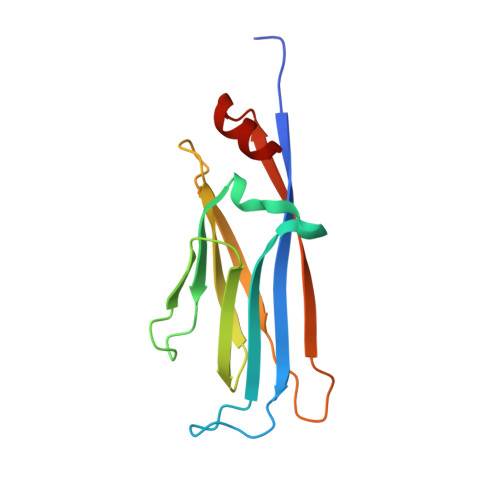
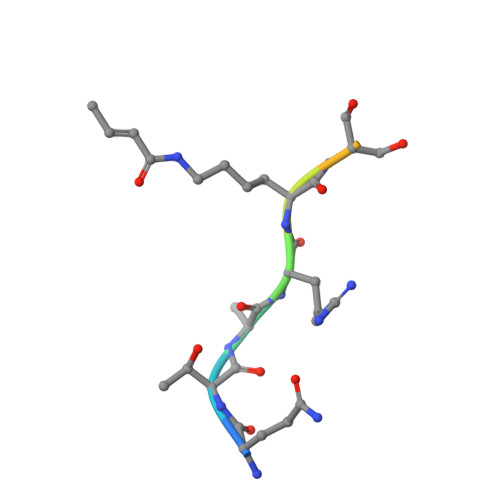
Structural insights into the pi-pi-pi stacking mechanism and DNA-binding activity of the YEATS domain.
Klein, B.J., Vann, K.R., Andrews, F.H., Wang, W.W., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Beloglazkina, A.A., Mi, W., Li, Y., Li, H., Shi, X., Kutateladze, A.G., Strahl, B.D., Liu, W.R., Kutateladze, T.G.(2018) Nat Commun 9: 4574-4574
- PubMed: 30385749
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07072-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6MIL, 6MIM, 6MIN, 6MIO, 6MIP, 6MIQ - PubMed Abstract:
The YEATS domain has been identified as a reader of histone acylation and more recently emerged as a promising anti-cancer therapeutic target. Here, we detail the structural mechanisms for π-π-π stacking involving the YEATS domains of yeast Taf14 and human AF9 and acylated histone H3 peptides and explore DNA-binding activities of these domains. Taf14-YEATS selects for crotonyllysine, forming π stacking with both the crotonyl amide and the alkene moiety, whereas AF9-YEATS exhibits comparable affinities to saturated and unsaturated acyllysines, engaging them through π stacking with the acyl amide. Importantly, AF9-YEATS is capable of binding to DNA, whereas Taf14-YEATS is not. Using a structure-guided approach, we engineered a mutant of Taf14-YEATS that engages crotonyllysine through the aromatic-aliphatic-aromatic π stacking and shows high selectivity for the crotonyl H3K9 modification. Our findings shed light on the molecular principles underlying recognition of acyllysine marks and reveal a previously unidentified DNA-binding activity of AF9-YEATS.
- Department of Pharmacology, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, CO, 80045, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: