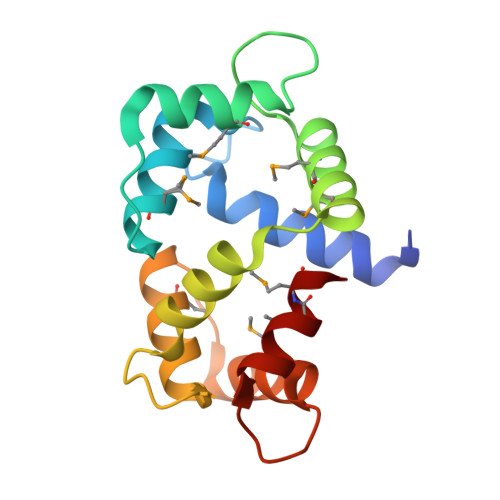
The CaMKII inhibitor KN93-calmodulin interaction and implications for calmodulin tuning of NaV1.5 and RyR2 function.
Johnson, C.N., Pattanayek, R., Potet, F., Rebbeck, R.T., Blackwell, D.J., Nikolaienko, R., Sequeira, V., Le Meur, R., Radwanski, P.B., Davis, J.P., Zima, A.V., Cornea, R.L., Damo, S.M., Gyorke, S., George Jr., A.L., Knollmann, B.C.(2019) Cell Calcium 82: 102063-102063
- PubMed: 31401388
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2019.102063
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6M7H - PubMed Abstract:
Here we report the structure of the widely utilized calmodulin (CaM)-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) inhibitor KN93 bound to the Ca 2+ -sensing protein CaM. KN93 is widely believed to inhibit CaMKII by binding to the kinase. The CaM-KN93 interaction is significant as it can interfere with the interaction between CaM and it's physiological targets, thereby raising the possibility of ascribing modified protein function to CaMKII phosphorylation while concealing a CaM-protein interaction. NMR spectroscopy, stopped-flow kinetic measurements, and x-ray crystallography were used to characterize the structure and biophysical properties of the CaM-KN93 interaction. We then investigated the functional properties of the cardiac Na + channel (Na V 1.5) and ryanodine receptor (RyR2). We find that KN93 disrupts a high affinity CaM-Na V 1.5 interaction and alters channel function independent of CaMKII. Moreover, KN93 increases RyR2 Ca 2+ release in cardiomyocytes independent of CaMKII. Therefore, when interpreting KN93 data, targets other than CaMKII need to be considered.
- Center for Arrhythmia Research and Therapeutics, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN 37240, USA; Dorothy M. Davis Heart and Lung Research Institute, College of Medicine, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH, USA. Electronic address: cn.johnson@vumc.org.
Organizational Affiliation: