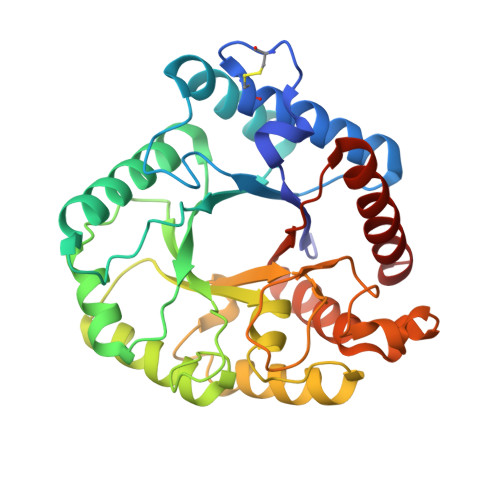
A unique DNA-binding mode of African swine fever virus AP endonuclease.
Chen, Y., Chen, X., Huang, Q., Shao, Z., Gao, Y., Li, Y., Yang, C., Liu, H., Li, J., Wang, Q., Ma, J., Zhang, Y.Z., Gu, Y., Gan, J.(2020) Cell Discov 6: 13-13
- PubMed: 32194979
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41421-020-0146-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6KHY, 6KI3 - PubMed Abstract:
African swine fever virus (ASFV) is highly contagious and can cause lethal disease in pigs. ASFV is primarily replicated in the cytoplasm of pig macrophages, which is oxidative and caused constant damage to ASFV genome. ASFV AP endonuclease ( Asfv AP) catalyzes DNA cleavage reaction at the abasic site and is a key enzyme of ASFV base excision repair (BER) system. Although it plays an essential role in ASFV survival in host cells, the basis underlying substrate binding and cleavage by Asfv AP remains unclear. Here, we reported the structural and functional studies of Asfv AP, showing that Asfv AP adopts a novel DNA-binding mode distinct from other APs. Asfv AP possesses many unique structural features, including one narrower nucleotide-binding pocket at the active site, the C16-C20 disulfide bond-containing region, and histidine-rich loop. As indicated by our mutagenesis, in vitro binding and cleavage assays, these features are important for Asfv AP to suit the acidic and oxidative environment. Owing to their functional importance, these unique features could serve as targets for designing small molecule inhibitors that could disrupt the repair process of ASFV genome and help fight against this deadly virus in the future.
- 1State Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering, Collaborative Innovation Center of Genetics and Development, Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, School of Life Sciences, Fudan University, 200438 Shanghai, China.
Organizational Affiliation: