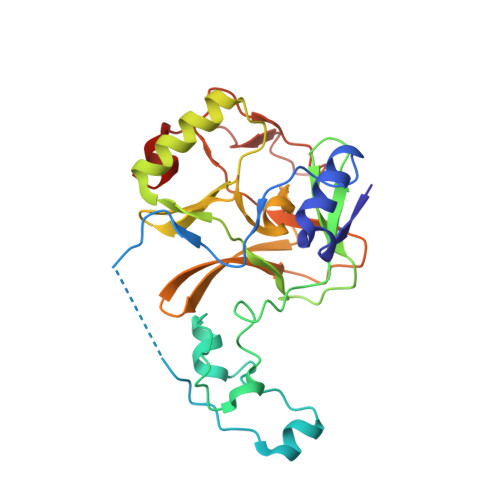
Histone H3.3 phosphorylation amplifies stimulation-induced transcription.
Armache, A., Yang, S., Martinez de Paz, A., Robbins, L.E., Durmaz, C., Cheong, J.Q., Ravishankar, A., Daman, A.W., Ahimovic, D.J., Klevorn, T., Yue, Y., Arslan, T., Lin, S., Panchenko, T., Hrit, J., Wang, M., Thudium, S., Garcia, B.A., Korb, E., Armache, K.J., Rothbart, S.B., Hake, S.B., Allis, C.D., Li, H., Josefowicz, S.Z.(2020) Nature 583: 852-857
- PubMed: 32699416
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2533-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6J9J - PubMed Abstract:
Complex organisms can rapidly induce select genes in response to diverse environmental cues. This regulation occurs in the context of large genomes condensed by histone proteins into chromatin. The sensing of pathogens by macrophages engages conserved signalling pathways and transcription factors to coordinate the induction of inflammatory genes 1-3 . Enriched integration of histone H3.3, the ancestral histone H3 variant, is a general feature of dynamically regulated chromatin and transcription 4-7 . However, how chromatin is regulated at induced genes, and what features of H3.3 might enable rapid and high-level transcription, are unknown. The amino terminus of H3.3 contains a unique serine residue (Ser31) that is absent in 'canonical' H3.1 and H3.2. Here we show that this residue, H3.3S31, is phosphorylated (H3.3S31ph) in a stimulation-dependent manner along rapidly induced genes in mouse macrophages. This selective mark of stimulation-responsive genes directly engages the histone methyltransferase SETD2, a component of the active transcription machinery, and 'ejects' the elongation corepressor ZMYND11 8,9 . We propose that features of H3.3 at stimulation-induced genes, including H3.3S31ph, provide preferential access to the transcription apparatus. Our results indicate dedicated mechanisms that enable rapid transcription involving the histone variant H3.3, its phosphorylation, and both the recruitment and the ejection of chromatin regulators.
- Laboratory of Epigenetics and Immunity, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: