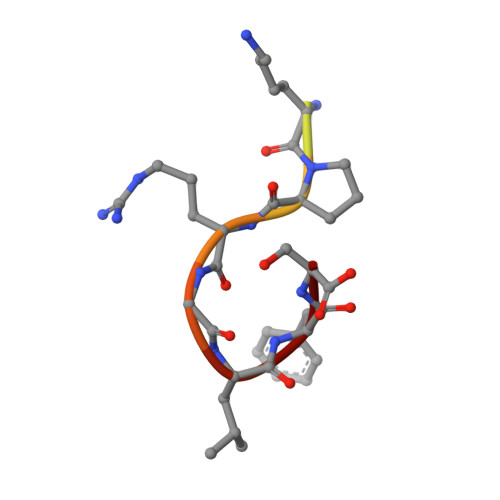
XLF and APLF bind Ku80 at two remote sites to ensure DNA repair by non-homologous end joining.
Nemoz, C., Ropars, V., Frit, P., Gontier, A., Drevet, P., Yu, J., Guerois, R., Pitois, A., Comte, A., Delteil, C., Barboule, N., Legrand, P., Baconnais, S., Yin, Y., Tadi, S., Barbet-Massin, E., Berger, I., Le Cam, E., Modesti, M., Rothenberg, E., Calsou, P., Charbonnier, J.B.(2018) Nat Struct Mol Biol 25: 971-980
- PubMed: 30291363
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-018-0133-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6ERF, 6ERG, 6ERH - PubMed Abstract:
The Ku70-Ku80 (Ku) heterodimer binds rapidly and tightly to the ends of DNA double-strand breaks and recruits factors of the non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) repair pathway through molecular interactions that remain unclear. We have determined crystal structures of the Ku-binding motifs (KBM) of the NHEJ proteins APLF (A-KBM) and XLF (X-KBM) bound to a Ku-DNA complex. The two KBM motifs bind remote sites of the Ku80 α/β domain. The X-KBM occupies an internal pocket formed by an unprecedented large outward rotation of the Ku80 α/β domain. We observe independent recruitment of the APLF-interacting protein XRCC4 and of XLF to laser-irradiated sites via binding of A- and X-KBMs, respectively, to Ku80. Finally, we show that mutation of the X-KBM and A-KBM binding sites in Ku80 compromises both the efficiency and accuracy of end joining and cellular radiosensitivity. A- and X-KBMs may represent two initial anchor points to build the intricate interaction network required for NHEJ.
- Institute for Integrative Biology of the Cell, Institute Joliot, CEA, CNRS, Université Paris-Sud, Université Paris-Saclay, Gif-sur-Yvette, France.
Organizational Affiliation: