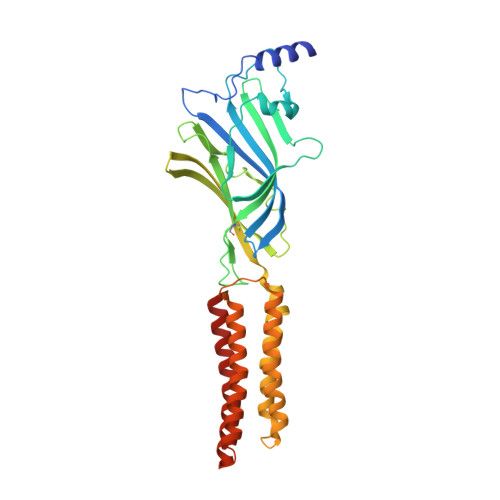
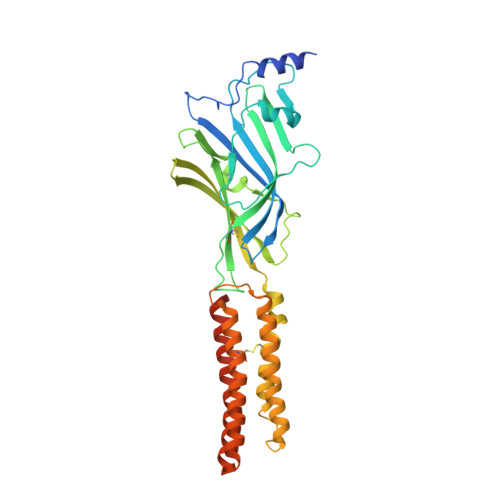
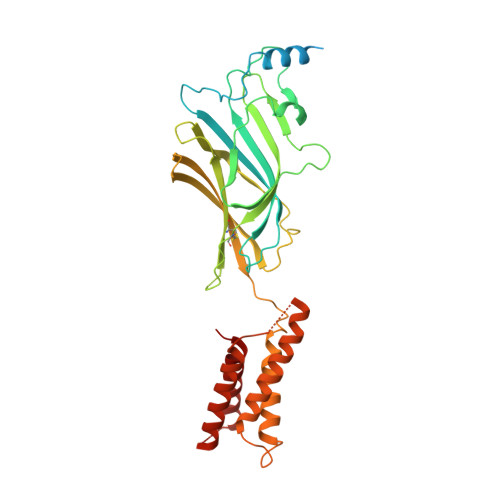
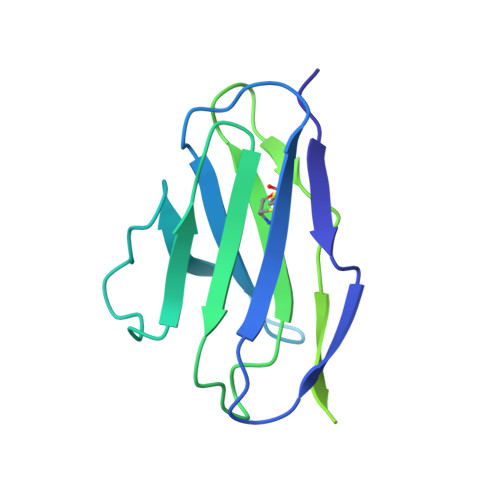
Structure of a human synaptic GABAAreceptor.
Zhu, S., Noviello, C.M., Teng, J., Walsh, R.M., Kim, J.J., Hibbs, R.E.(2018) Nature 559: 67-72
- PubMed: 29950725
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0255-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6D6T, 6D6U - PubMed Abstract:
Fast inhibitory neurotransmission in the brain is principally mediated by the neurotransmitter GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) and its synaptic target, the type A GABA receptor (GABA A receptor). Dysfunction of this receptor results in neurological disorders and mental illnesses including epilepsy, anxiety and insomnia. The GABA A receptor is also a prolific target for therapeutic, illicit and recreational drugs, including benzodiazepines, barbiturates, anaesthetics and ethanol. Here we present high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures of the human α1β2γ2 GABA A receptor, the predominant isoform in the adult brain, in complex with GABA and the benzodiazepine site antagonist flumazenil, the first-line clinical treatment for benzodiazepine overdose. The receptor architecture reveals unique heteromeric interactions for this important class of inhibitory neurotransmitter receptor. This work provides a template for understanding receptor modulation by GABA and benzodiazepines, and will assist rational approaches to therapeutic targeting of this receptor for neurological disorders and mental illness.
- Departments of Neuroscience and Biophysics, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: