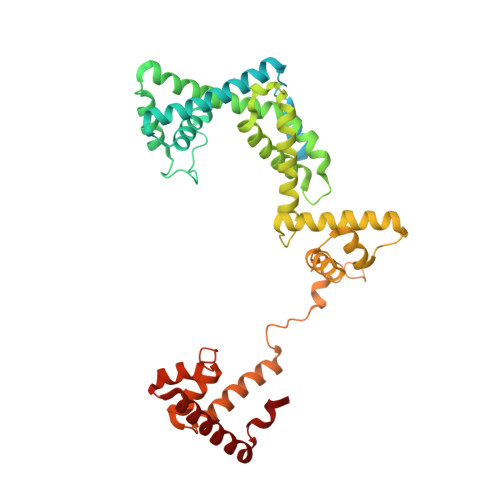
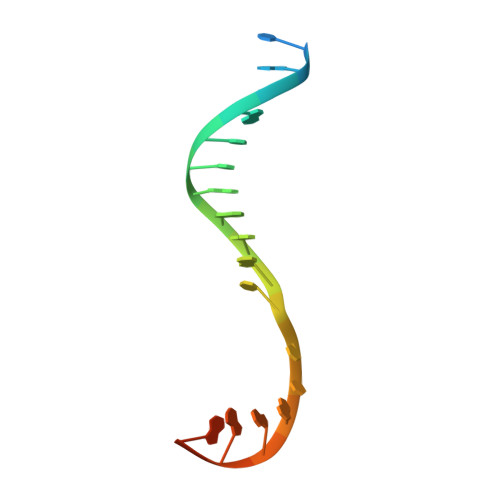
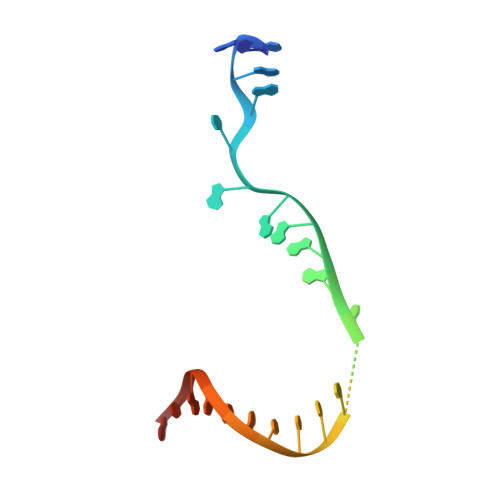
Mode of Action of Kanglemycin A, an Ansamycin Natural Product that Is Active against Rifampicin-Resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Mosaei, H., Molodtsov, V., Kepplinger, B., Harbottle, J., Moon, C.W., Jeeves, R.E., Ceccaroni, L., Shin, Y., Morton-Laing, S., Marrs, E.C.L., Wills, C., Clegg, W., Yuzenkova, Y., Perry, J.D., Bacon, J., Errington, J., Allenby, N.E.E., Hall, M.J., Murakami, K.S., Zenkin, N.(2018) Mol Cell 72: 263-274.e5
- PubMed: 30244835
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.08.028
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6CUU, 6CUX - PubMed Abstract:
Antibiotic-resistant bacterial pathogens pose an urgent healthcare threat, prompting a demand for new medicines. We report the mode of action of the natural ansamycin antibiotic kanglemycin A (KglA). KglA binds bacterial RNA polymerase at the rifampicin-binding pocket but maintains potency against RNA polymerases containing rifampicin-resistant mutations. KglA has antibiotic activity against rifampicin-resistant Gram-positive bacteria and multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MDR-M. tuberculosis). The X-ray crystal structures of KglA with the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme and Thermus thermophilus RNA polymerase-promoter complex reveal an altered-compared with rifampicin-conformation of KglA within the rifampicin-binding pocket. Unique deoxysugar and succinate ansa bridge substituents make additional contacts with a separate, hydrophobic pocket of RNA polymerase and preclude the formation of initial dinucleotides, respectively. Previous ansa-chain modifications in the rifamycin series have proven unsuccessful. Thus, KglA represents a key starting point for the development of a new class of ansa-chain derivatized ansamycins to tackle rifampicin resistance.
- Centre for Bacterial Cell Biology, Institute for Cell and Molecular Biosciences, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne NE2 4AX, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: