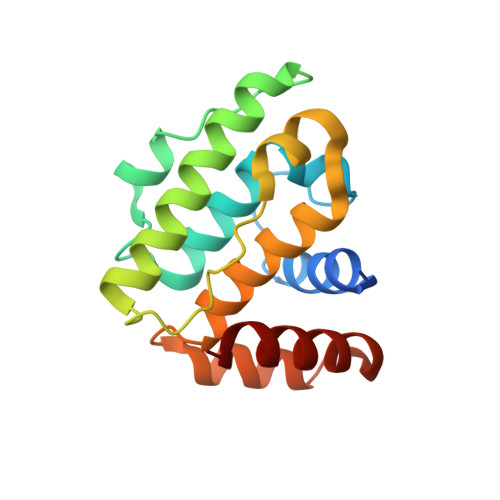
A conserved interaction of the dynein light intermediate chain with dynein-dynactin effectors necessary for processivity.
Lee, I.G., Olenick, M.A., Boczkowska, M., Franzini-Armstrong, C., Holzbaur, E.L.F., Dominguez, R.(2018) Nat Commun 9: 986-986
- PubMed: 29515126
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03412-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6B9H - PubMed Abstract:
Cytoplasmic dynein is the major minus-end-directed microtubule-based motor in cells. Dynein processivity and cargo selectivity depend on cargo-specific effectors that, while generally unrelated, share the ability to interact with dynein and dynactin to form processive dynein-dynactin-effector complexes. How this is achieved is poorly understood. Here, we identify a conserved region of the dynein Light Intermediate Chain 1 (LIC1) that mediates interactions with unrelated dynein-dynactin effectors. Quantitative binding studies map these interactions to a conserved helix within LIC1 and to N-terminal fragments of Hook1, Hook3, BICD2, and Spindly. A structure of the LIC1 helix bound to the N-terminal Hook domain reveals a conformational change that creates a hydrophobic cleft for binding of the LIC1 helix. The LIC1 helix competitively inhibits processive dynein-dynactin-effector motility in vitro, whereas structure-inspired mutations in this helix impair lysosomal positioning in cells. The results reveal a conserved mechanism of effector interaction with dynein-dynactin necessary for processive motility.
- Department of Physiology, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, 19104, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: