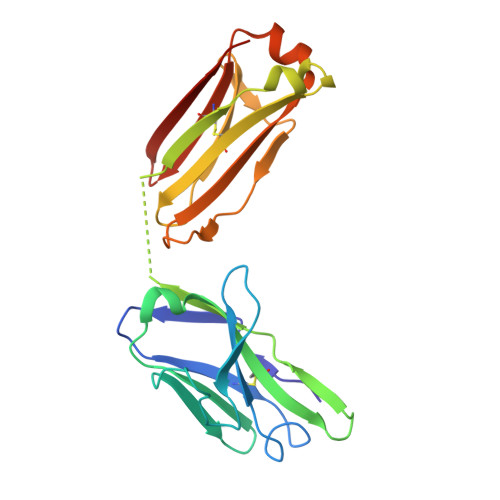
Structural Definition of a Unique Neutralization Epitope on the Receptor-Binding Domain of MERS-CoV Spike Glycoprotein
Zhang, S., Zhou, P., Wang, P., Li, Y., Jiang, L., Jia, W., Wang, H., Fan, A., Wang, D., Shi, X., Fang, X., Hammel, M., Wang, S., Wang, X., Zhang, L.(2018) Cell Rep 24: 441-452
- PubMed: 29996104
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.06.041
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5YY5, 5ZXV - PubMed Abstract:
The major mechanism of antibody-mediated neutralization of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) involves competition with the cellular receptor dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) for binding to the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the spike (S) glycoprotein. Here, we report a unique epitope and unusual neutralizing mechanism of the isolated human antibody MERS-4. Structurally, MERS-4 approached the RBD from the outside of the RBD-DPP4 binding interface. Such binding resulted in the folding of the β5-β6 loop toward a shallow groove on the RBD interface critical for accommodating DPP4. The key residues for binding are identified through site-directed mutagenesis. Structural modeling revealed that MERS-4 binds to RBD only in the "up" position in the S trimer. Furthermore, MERS-4 demonstrated synergy with several reported antibodies. These results indicate that MERS-4 neutralizes MERS-CoV by indirect rather than direct competition with DPP4. This mechanism provides a valuable addition for the combined use of antibodies against MERS-CoV infection.
- The Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Protein Science, Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology, Collaborative Innovation Center for Biotherapy, School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China.
Organizational Affiliation: