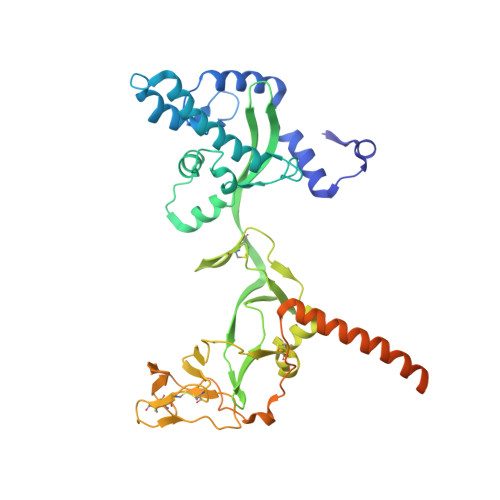
Structures of the prefusion form of measles virus fusion protein in complex with inhibitors.
Hashiguchi, T., Fukuda, Y., Matsuoka, R., Kuroda, D., Kubota, M., Shirogane, Y., Watanabe, S., Tsumoto, K., Kohda, D., Plemper, R.K., Yanagi, Y.(2018) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115: 2496-2501
- PubMed: 29463726
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1718957115
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5YXW, 5YZC, 5YZD - PubMed Abstract:
Measles virus (MeV), a major cause of childhood morbidity and mortality, is highly immunotropic and one of the most contagious pathogens. MeV may establish, albeit rarely, persistent infection in the central nervous system, causing fatal and intractable neurodegenerative diseases such as subacute sclerosing panencephalitis and measles inclusion body encephalitis. Recent studies have suggested that particular substitutions in the MeV fusion (F) protein are involved in the pathogenesis by destabilizing the F protein and endowing it with hyperfusogenicity. Here we show the crystal structures of the prefusion MeV-F alone and in complex with the small compound AS-48 or a fusion inhibitor peptide. Notably, these independently developed inhibitors bind the same hydrophobic pocket located at the region connecting the head and stalk of MeV-F, where a number of substitutions in MeV isolates from neurodegenerative diseases are also localized. Since these inhibitors could suppress membrane fusion mediated by most of the hyperfusogenic MeV-F mutants, the development of more effective inhibitors based on the structures may be warranted to treat MeV-induced neurodegenerative diseases.
- Department of Virology, Faculty of Medicine, Kyushu University, 812-8582 Fukuoka, Japan; takaoh@virology.med.kyushu-u.ac.jp yyanagi@virology.med.kyushu-u.ac.jp.
Organizational Affiliation: