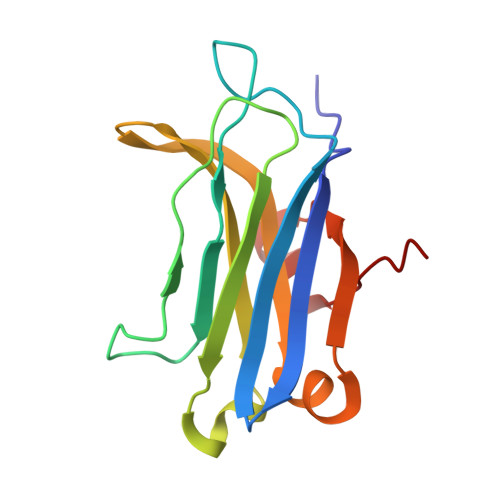
Structural Basis of Protein Kinase C alpha Regulation by the C-Terminal Tail.
Yang, Y., Shu, C., Li, P., Igumenova, T.I.(2018) Biophys J 114: 1590-1603
- PubMed: 29642029
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2017.12.030
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5W4S - PubMed Abstract:
Protein kinase C (PKC) isoenzymes are multi-modular proteins activated at the membrane surface to regulate signal transduction processes. When activated by second messengers, PKC undergoes a drastic conformational and spatial transition from the inactive cytosolic state to the activated membrane-bound state. The complete structure of either state of PKC remains elusive. We demonstrate, using NMR spectroscopy, that the isolated Ca 2+ -sensing membrane-binding C2 domain of the conventional PKCα interacts with a conserved hydrophobic motif of the kinase C-terminal region, and we report a structural model of the complex. Our data suggest that the C-terminal region plays a dual role in regulating the PKC activity: activating, through sensitization of PKC to intracellular Ca 2+ oscillations; and auto-inhibitory, through its interaction with a conserved positively charged region of the C2 domain.
- Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas.
Organizational Affiliation: