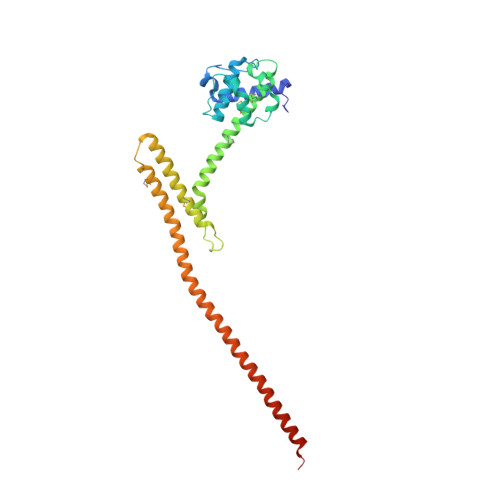
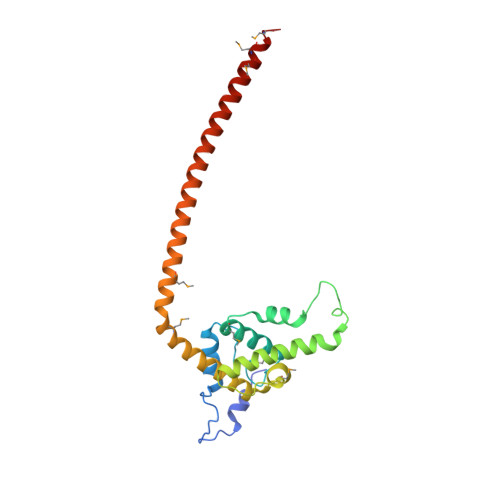
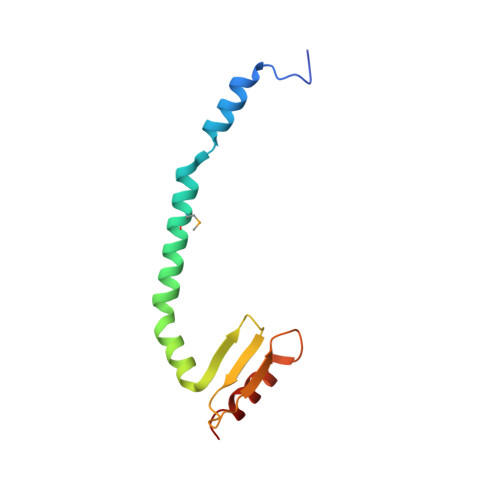
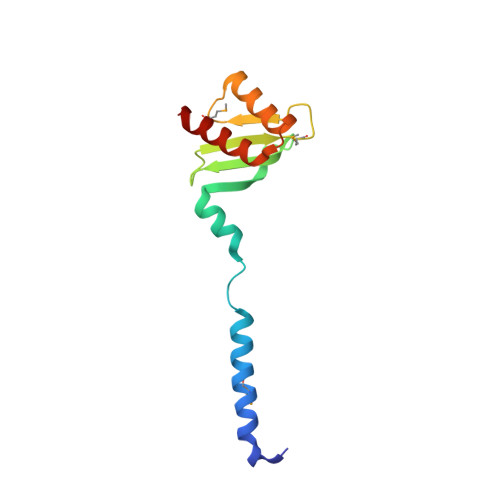
Conserved Tetramer Junction in the Kinetochore Ndc80 Complex.
Valverde, R., Ingram, J., Harrison, S.C.(2016) Cell Rep 17: 1915-1922
- PubMed: 27851957
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.10.065
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5TCS, 5TD8 - PubMed Abstract:
The heterotetrameric Ndc80 complex establishes connectivity along the principal longitudinal axis of a kinetochore. Its two heterodimeric subcomplexes, each with a globular end and a coiled-coil shaft, connect end-to-end to create a ∼600 Å long rod spanning the gap from centromere-proximal structures to spindle microtubules. Neither subcomplex has a known function on its own, but the heterotetrameric organization and the characteristics of the junction are conserved from yeast to man. We have determined crystal structures of two shortened ("dwarf") Ndc80 complexes that contain the full tetramer junction and both globular ends. The junction connects two α-helical coiled coils through regions of four-chain and three-chain overlap. The complexity of its structure depends on interactions among conserved amino-acid residues, suggesting a binding site for additional cellular factor(s) not yet identified.
- Department of Biological Chemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, Harvard Medical School, and Howard Hughes Medical Institute, 250 Longwood Avenue, Boston, MA 02115, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: