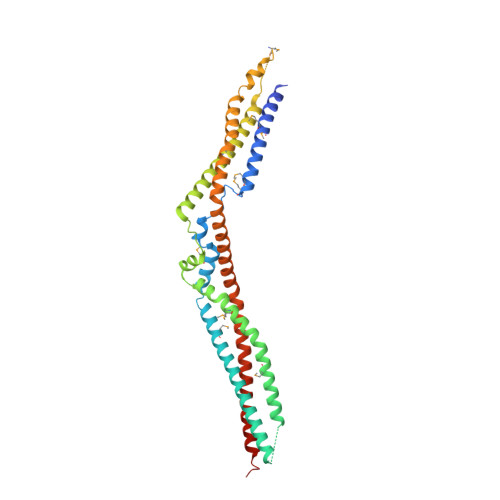
Structural Basis for Selective Interaction between the ESCRT Regulator HD-PTP and UBAP1.
Gahloth, D., Levy, C., Heaven, G., Stefani, F., Wunderley, L., Mould, P., Cliff, M.J., Bella, J., Fielding, A.J., Woodman, P., Tabernero, L.(2016) Structure 24: 2115-2126
- PubMed: 27839950
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2016.10.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5LM1, 5LM2 - PubMed Abstract:
Endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRTs) are essential for ubiquitin-dependent degradation of mitogenic receptors, a process often compromised in cancer pathologies. Sorting of ubiquinated receptors via ESCRTs is controlled by the tumor suppressor phosphatase HD-PTP. The specific interaction between HD-PTP and the ESCRT-I subunit UBAP1 is critical for degradation of growth factor receptors and integrins. Here, we present the structural characterization by X-ray crystallography and double electron-electron resonance spectroscopy of the coiled-coil domain of HD-PTP and its complex with UBAP1. The coiled-coil domain adopts an unexpected open and rigid conformation that contrasts with the closed and flexible coiled-coil domain of the related ESCRT regulator Alix. The HD-PTP:UBAP1 structure identifies the molecular determinants of the interaction and provides a molecular basis for the specific functional cooperation between HD-PTP and UBAP1. Our findings provide insights into the molecular mechanisms of regulation of ESCRT pathways that could be relevant to anticancer therapies.
- School of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Biology, Medicine and Health, University of Manchester, Manchester M13 9PT, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: