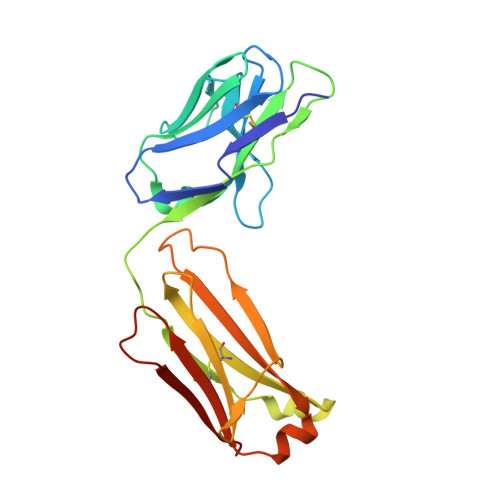
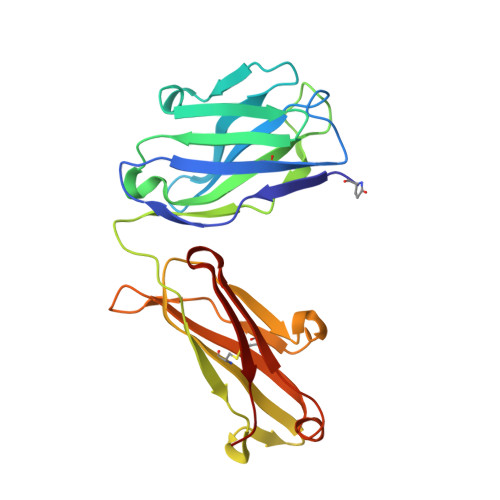
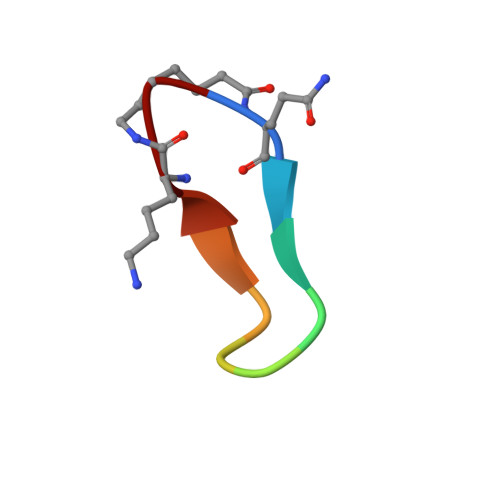
Cyclization strategies of meditopes: affinity and diffraction studies of meditope-Fab complexes.
Bzymek, K.P., Ma, Y., Avery, K.A., Horne, D.A., Williams, J.C.(2016) Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 72: 434-442
- PubMed: 27303895
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X16007202
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5ESQ, 5HPM, 5HYQ, 5ICX, 5ICY, 5ICZ, 5ID0, 5ID1 - PubMed Abstract:
Recently, a unique binding site for a cyclic 12-residue peptide was discovered within a cavity formed by the light and heavy chains of the cetuximab Fab domain. In order to better understand the interactions that drive this unique complex, a number of variants including the residues within the meditope peptide and the antibody, as well as the cyclization region of the meditope peptide, were created. Here, multiple crystal structures of meditope peptides incorporating different cyclization strategies bound to the central cavity of the cetuximab Fab domain are presented. The affinity of each cyclic derivative for the Fab was determined by surface plasmon resonance and correlated to structural differences. Overall, it was observed that the disulfide bond used to cyclize the peptide favorably packs against a hydrophobic `pocket' and that amidation and acetylation of the original disulfide meditope increased the overall affinity ∼2.3-fold. Conversely, replacing the terminal cysteines with serines and thus creating a linear peptide reduced the affinity over 50-fold, with much of this difference being reflected in a decrease in the on-rate. Other cyclization methods, including the formation of a lactam, reduced the affinity but not to the extent of the linear peptide. Collectively, the structural and kinetic data presented here indicate that small perturbations introduced by different cyclization strategies can significantly affect the affinity of the meditope-Fab complex.
- Department of Molecular Medicine, Beckman Research Institute of City of Hope, 1710 Flower Street, Duarte, CA 91010, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: