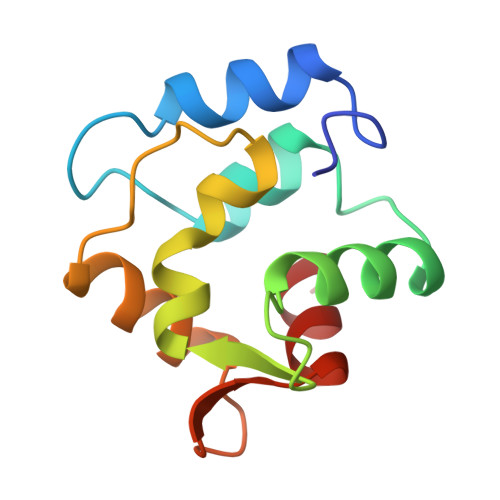
Restrained least squares refinement of native (calcium) and cadmium-substituted carp parvalbumin using X-ray crystallographic data at 1.6-A resolution.
Swain, A.L., Kretsinger, R.H., Amma, E.L.(1989) J Biological Chem 264: 16620-16628
- PubMed: 2777802
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1CDP, 5CPV - PubMed Abstract:
Carp parvalbumin coordinates calcium through one carbonyl oxygen atom and the oxygen-containing side chains of 5 amino acid residues, or 4 residues and a water molecule, in a helix-loop-helix structural motif. Other calcium-binding proteins, including calmodulin and troponin C, also possess this unique calcium-binding design, which is designated EF-hand or calmodulin fold. Parvalbumin has two such sites, labeled CD and EF. Each of the calcium-binding sites of refined structures of proteins belonging to this group has a 7-oxygen coordination sphere except those of the structure of parvalbumin as it was reported in 1975. This structure had been refined at 1.9 A using difference Fourier techniques on film data. The CD site appeared to be 6-coordinate and the EF site 8-coordinate. Results of NMR experiments using 113Cd-substituted parvalbumin, however, indicate that the sites are similar to one another with coordination number greater than 6. To resolve the inconsistency between crystallographic and NMR results, 1.6 A area detector data was collected for native and cadmium-substituted parvalbumin; the structures have been refined to R factors of 18.7% and 16.4%, respectively, with acceptable geometry and low errors in atomic coordinates. Differences between the parvalbumin structure described in 1975 and the present structure are addressed, including the discovery of 7-coordination for both the CD and EF sites.
- Department of Chemistry, University of South Carolina, Columbia 29208.
Organizational Affiliation: