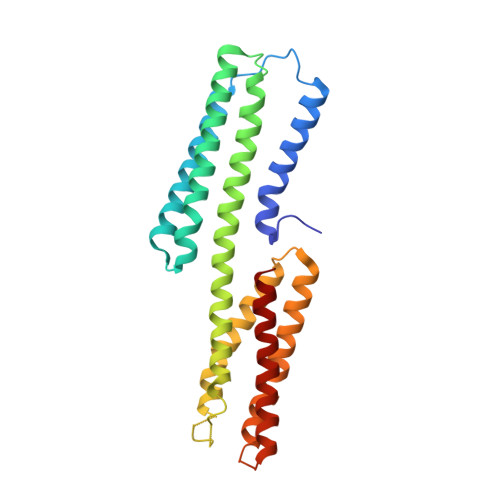
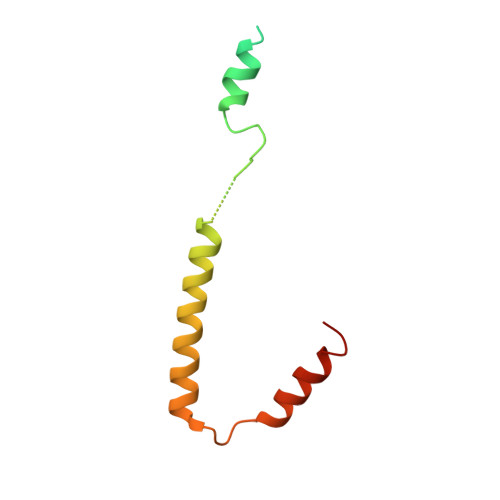
The force-sensing device region of alpha-catenin is an intrinsically disordered segment in the absence of intramolecular stabilization of the autoinhibitory form
Hirano, Y., Amano, Y., Yonemura, S., Hakoshima, T.(2018) Genes Cells 23: 370-385
- PubMed: 29542234
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/gtc.12578
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5XFL, 5Y04 - PubMed Abstract:
Mechanotransduction by α-catenin facilitates the force-dependent development of adherens junctions (AJs) by recruiting vinculin to reinforce actin anchoring of AJs. The α-catenin mechanotransducing action is facilitated by its force-sensing device region that autoinhibits the vinculin-binding site 1 (VBS1). Here, we report the high-resolution structure of the force-sensing device region of α-catenin, which shows the autoinhibited form comprised of helix bundles E, F and G. The cryptic VBS1 is embedded into helix bundle E stabilized by direct interactions with the autoinhibitory region forming helix bundles F and G. Our molecular dissection study showed that helix bundles F and G are stable in solution in each isolated form, whereas helix bundle E that contains VBS1 is unstable and intrinsically disordered in solution in the isolated form. We successfully identified key residues mediating the autoinhibition and produced mutated α-catenins that display variable force sensitivity and autoinhibition. Using these mutants, we demonstrate both in vitro and in vivo that, in the absence of this stabilization, the helix bundle containing VBS1 would adopt an unfolded form, thus exposing VBS for vinculin binding. We provide evidence for importance of mechanotransduction with the intrinsic force sensitivity for vinculin recruitment to adherens junctions of epithelial cell sheets with mutated α-catenins.
- Structural Biology Laboratory, Nara Institute of Science and Technology, Ikoma, Nara, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: