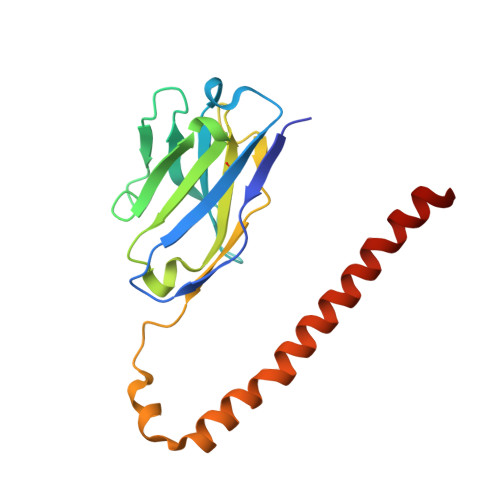
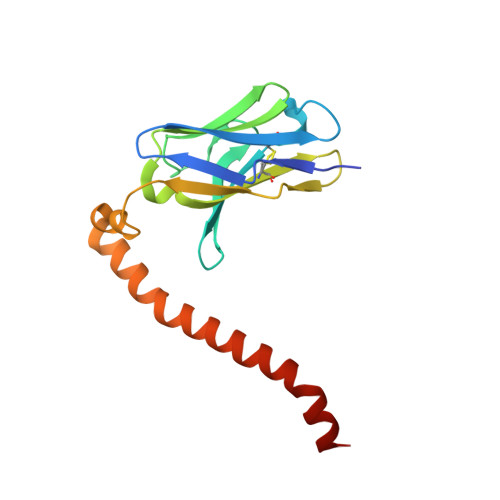
Fv-clasp: An Artificially Designed Small Antibody Fragment with Improved Production Compatibility, Stability, and Crystallizability
Arimori, T., Kitago, Y., Umitsu, M., Fujii, Y., Asaki, R., Tamura-Kawakami, K., Takagi, J.(2017) Structure 25: 1611-1622.e4
- PubMed: 28919443
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2017.08.011
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5XCQ, 5XCR, 5XCS, 5XCT, 5XCU, 5XCV, 5XCX - PubMed Abstract:
Antibody fragments are frequently used as a "crystallization chaperone" to aid structural analysis of complex macromolecules that are otherwise crystallization resistant, but conventional fragment formats have not been designed for this particular application. By fusing an anti-parallel coiled-coil structure derived from the SARAH domain of human Mst1 kinase to the variable region of an antibody, we succeeded in creating a novel chimeric antibody fragment of ∼37 kDa, termed "Fv-clasp," which exhibits excellent crystallization compatibility while maintaining the binding ability of the original IgG molecule. The "clasp" and the engineered disulfide bond at the bottom of the Fv suppressed the internal mobility of the fragment and shielded hydrophobic residues, likely contributing to the high heat stability and the crystallizability of the Fv-clasp. Finally, Fv-clasp antibodies showed superior "chaperoning" activity over conventional Fab fragments, and facilitated the structure determination of an ectodomain fragment of integrin α6β1.
- Institute for Protein Research, Osaka University, Suita, Osaka 565-0871, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: