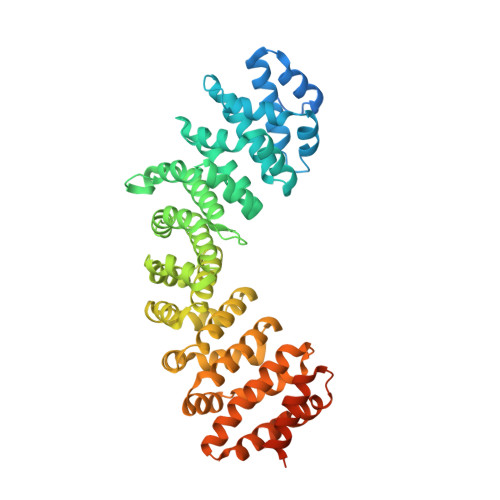
Zika virus NS5 forms supramolecular nuclear bodies that sequester importin alpha and modulate the host immune and pro-inflammatory response in neuronal cells.
Ng, I.H.W., Chan, K., Tan, M.J.A., Gwee, C.P., Smith, K.M., Jeffress, S.J., Saw, W.G., Swarbrick, C.M.D., Watanabe, S., Jans, D., Gruber, G., Forwood, J.K., Vasudevan, S.G.(2019) ACS Infect Dis
- PubMed: 30848123
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsinfecdis.8b00373
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5W41 - PubMed Abstract:
The Zika virus (ZIKV) epidemic in the Americas was alarming because of its link with microcephaly in neonates and Guillain-Barré syndrome in adults. The unusual pathologies induced by ZIKV infection and the knowledge that the flaviviral nonstructural protein 5 (NS5), the most conserved protein in the flavivirus proteome, can modulate the host immune response during ZIKV infection prompted us to investigate the subcellular localization of NS5 during ZIKV infection and explore its functional significance. A monopartite nuclear localization signal (NLS) sequence within ZIKV NS5 was predicted by the cNLS Mapper program, and we observed localization of ZIKV NS5 in the nucleus of infected cells by immunostaining with specific antibodies. Strikingly, ZIKV NS5 forms spherical shell-like nuclear bodies that exclude DNA. The putative monopartite NLS 390 KRPR 393 is necessary to direct FLAG-tagged NS5 to the nucleus as the NS5 390 ARPA 393 mutant protein accumulates in the cytoplasm. Furthermore, coimmunostaining experiments reveal that NS5 localizes with and sequesters importin-α, but not importin-β, in the observed nuclear bodies during virus infection. Structural and biochemical data demonstrate binding of ZIKV NS5 with importin-α and reveal important binding determinants required for their interaction and formation of complexes that give rise to the supramolecular nuclear bodies. Significantly, we demonstrate a neuronal-specific activation of the host immune response to ZIKV infection and a possible role of ZIKV NS5's nuclear localization toward this activation. This suggests that ZIKV pathogenesis may arise from a tissue-specific host response to ZIKV infection.
- Program in Emerging Infectious Diseases , Duke-NUS Medical School , 8 College Road , Singapore 169857.
Organizational Affiliation: