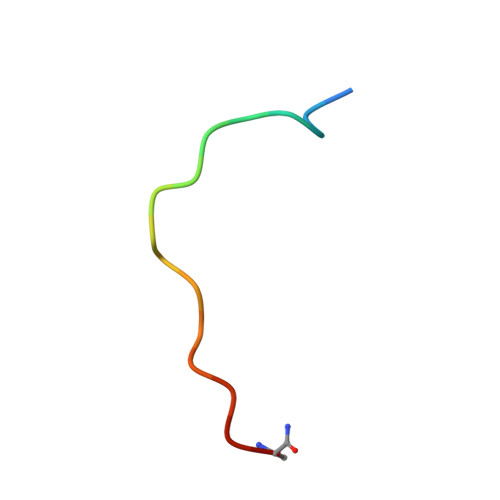
A coiled conformation of amyloid-beta recognized by antibody C706.
Teplyakov, A., Obmolova, G., Gilliland, G.L.(2017) Alzheimers Res Ther 9: 66-66
- PubMed: 28830506
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-017-0296-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5W3P - PubMed Abstract:
β-Amyloid (Aβ) peptide is believed to play a pivotal role in the development of Alzheimer's disease. Passive immunization with anti-Aβ monoclonal antibodies may facilitate the clearance of Aβ in the brain and may thus prevent the downstream pathology. Antibodies targeting the immunodominant N-terminal epitope of Aβ and capable of binding both the plaques and soluble species have been most efficacious in animal models. Structural studies of such antibodies with bound Aβ peptides provided the basis for understanding the mechanisms of action and the differences in potency. To gain further insight into the structural determinants of antigen recognition and the preferential Aβ conformations, we determined the crystal structure of murine antibody C706 in complex with the N-terminal Aβ 1-16 peptide sequence. The antigen-binding fragment of C706 was expressed in HEK293 cells and was crystallized in complex with the Aβ peptide. The X-ray structure was determined at 1.9-Å resolution. The binding epitope of C706 is centered on residues Arg5 and His6, which provide the majority of interactions. Unlike most antibodies, C706 recognizes a coiled rather than extended conformation of Aβ. Comparison with other antibodies targeting the N-terminal section of Aβ suggests that the conformation of the bound peptide may be linked to the immunization protocol and may reflect the preference for the extended conformation in the context of a longer Aβ peptide as opposed to the coiled conformation in the isolated short peptide.
- Janssen Research and Development, LLC, 1400 McKean Road, Spring House, PA, 19477, USA. janssen.biotech@usa.com.
Organizational Affiliation: