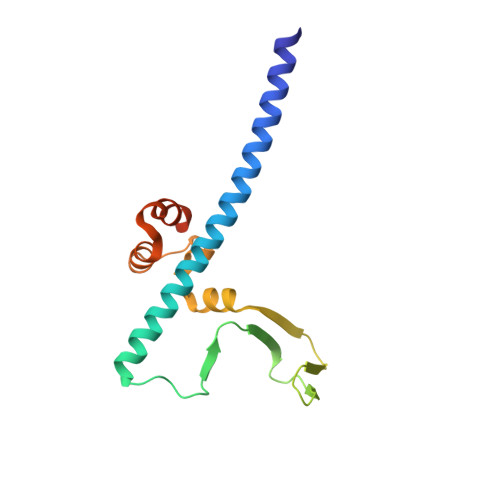
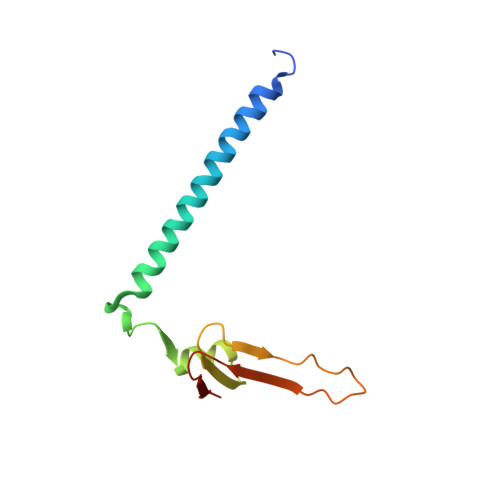
Conservation and divergence of C-terminal domain structure in the retinoblastoma protein family.
Liban, T.J., Medina, E.M., Tripathi, S., Sengupta, S., Henry, R.W., Buchler, N.E., Rubin, S.M.(2017) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114: 4942-4947
- PubMed: 28439018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1619170114
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5TUU, 5TUV - PubMed Abstract:
The retinoblastoma protein (Rb) and the homologous pocket proteins p107 and p130 negatively regulate cell proliferation by binding and inhibiting members of the E2F transcription factor family. The structural features that distinguish Rb from other pocket proteins have been unclear but are critical for understanding their functional diversity and determining why Rb has unique tumor suppressor activities. We describe here important differences in how the Rb and p107 C-terminal domains (CTDs) associate with the coiled-coil and marked-box domains (CMs) of E2Fs. We find that although CTD-CM binding is conserved across protein families, Rb and p107 CTDs show clear preferences for different E2Fs. A crystal structure of the p107 CTD bound to E2F5 and its dimer partner DP1 reveals the molecular basis for pocket protein-E2F binding specificity and how cyclin-dependent kinases differentially regulate pocket proteins through CTD phosphorylation. Our structural and biochemical data together with phylogenetic analyses of Rb and E2F proteins support the conclusion that Rb evolved specific structural motifs that confer its unique capacity to bind with high affinity those E2Fs that are the most potent activators of the cell cycle.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA 95064.
Organizational Affiliation: