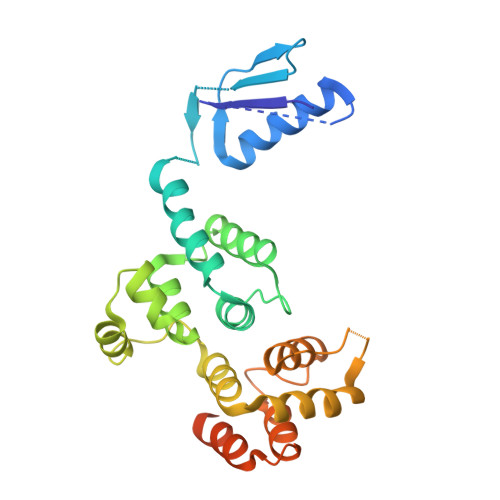
IKK gamma-Mimetic Peptides Block the Resistance to Apoptosis Associated with Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Infection.
Briggs, L.C., Chan, A.W.E., Davis, C.A., Whitelock, N., Hotiana, H.A., Baratchian, M., Bagneris, C., Selwood, D.L., Collins, M.K., Barrett, T.E.(2017) J Virol 91
- PubMed: 28931678
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01170-17
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5LDE - PubMed Abstract:
Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) is a lymphogenic disorder associated with Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) infection. Key to the survival and proliferation of PEL is the canonical NF-κB pathway, which becomes constitutively activated following overexpression of the viral oncoprotein KSHV vFLIP (ks-vFLIP). This arises from its capacity to form a complex with the modulatory subunit of the IκB kinase (IKK) kinase, IKKγ (or NEMO), resulting in the overproduction of proteins that promote cellular survival and prevent apoptosis, both of which are important drivers of tumorigenesis. Using a combination of cell-based and biophysical assays together with structural techniques, we showed that the observed resistance to cell death is largely independent of autophagy or major death receptor signaling pathways and demonstrated that direct targeting of the ks-vFLIP-IKKγ interaction both in cells and in vitro can be achieved using IKKγ-mimetic peptides. Our results further reveal that these peptides not only induce cell killing but also potently sensitize PEL to the proapoptotic agents tumor necrosis factor alpha and etoposide and are the first to confirm ks-vFLIP as a tractable target for the treatment of PEL and related disorders. IMPORTANCE KSHV vFLIP (ks-vFLIP) has been shown to have a crucial role in cellular transformation, in which it is vital for the survival and proliferation of primary effusion lymphoma (PEL), an aggressive malignancy associated with infection that is resistant to the majority of chemotherapeutic drugs. It operates via subversion of the canonical NF-κB pathway, which requires a physical interaction between ks-vFLIP and the IKK kinase modulatory subunit IKKγ. While this interaction has been directly linked to protection against apoptosis, it is unclear whether the suppression of other cell death pathways implicated in ks-vFLIP pathogenesis is an additional contributor. We demonstrate that the interaction between ks-vFLIP and IKKγ is pivotal in conferring resistance to apoptosis. Additionally, we show that the ks-vFLIP-IKKγ complex can be disrupted using peptides leading to direct killing and the sensitization of PEL cells to proapoptotic agents. Our studies thus provide a framework for future therapeutic interventions.
- Institute for Structural and Molecular Biology, Department of Biological Sciences, Birkbeck College, London, United Kingdom.
Organizational Affiliation: