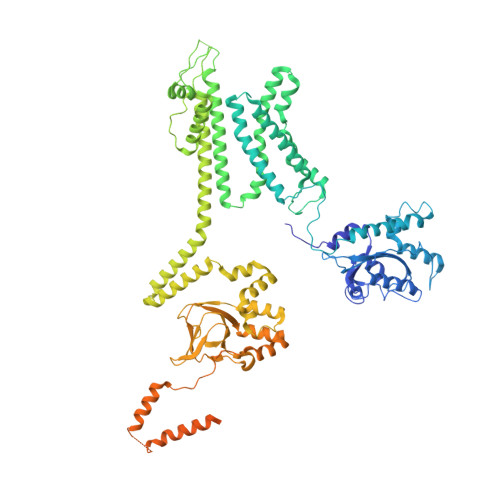
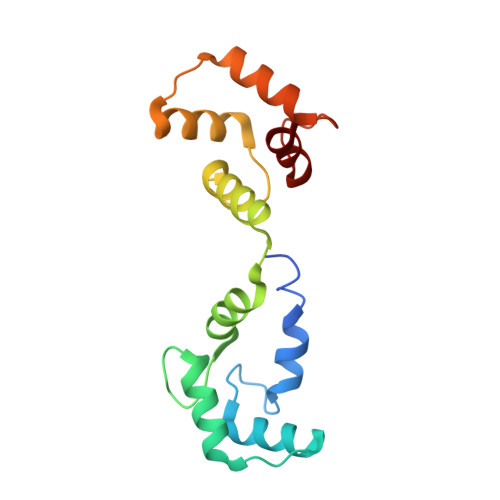
Structure of the voltage-gated K+ channel Eag1 reveals an alternative voltage sensing mechanism.
Whicher, J.R., MacKinnon, R.(2016) Science 353: 664-669
- PubMed: 27516594
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf8070
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5K7L - PubMed Abstract:
Voltage-gated potassium (K(v)) channels are gated by the movement of the transmembrane voltage sensor, which is coupled, through the helical S4-S5 linker, to the potassium pore. We determined the single-particle cryo-electron microscopy structure of mammalian K(v)10.1, or Eag1, bound to the channel inhibitor calmodulin, at 3.78 angstrom resolution. Unlike previous K(v) structures, the S4-S5 linker of Eag1 is a five-residue loop and the transmembrane segments are not domain swapped, which suggest an alternative mechanism of voltage-dependent gating. Additionally, the structure and position of the S4-S5 linker allow calmodulin to bind to the intracellular domains and to close the potassium pore, independent of voltage-sensor position. The structure reveals an alternative gating mechanism for K(v) channels and provides a template to further understand the gating properties of Eag1 and related channels.
- Laboratory of Molecular Neurobiology and Biophysics, The Rockefeller University, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, 1230 York Avenue, New York, NY 10065, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: