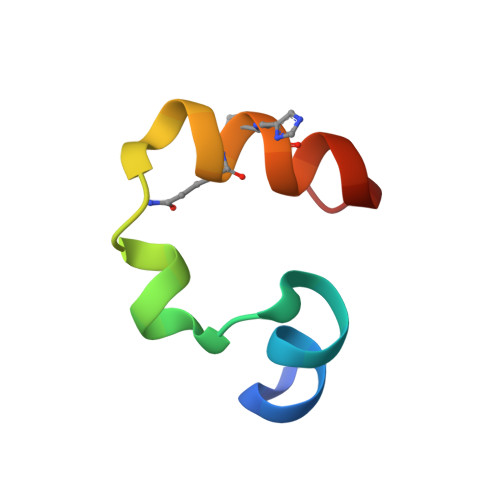
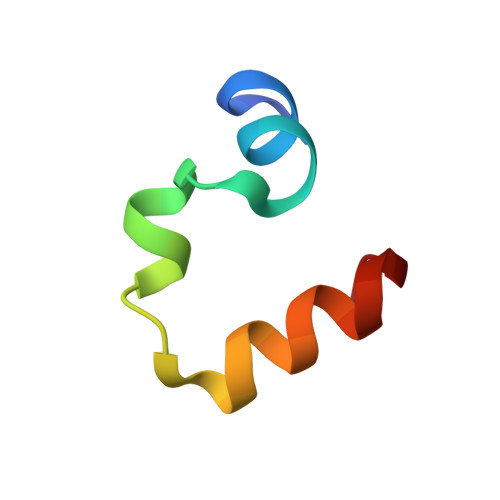
Effects of Single alpha-to-beta Residue Replacements on Structure and Stability in a Small Protein: Insights from Quasiracemic Crystallization.
Kreitler, D.F., Mortenson, D.E., Forest, K.T., Gellman, S.H.(2016) J Am Chem Soc 138: 6498-6505
- PubMed: 27171550
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b01454
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5I1N, 5I1O, 5I1P, 5I1S - PubMed Abstract:
Synthetic peptides that contain backbone modifications but nevertheless adopt folded structures similar to those of natural polypeptides are of fundamental interest and may provide a basis for biomedical applications. Such molecules can, for example, mimic the ability of natural prototypes to bind to specific target macromolecules but resist degradation by proteases. We have previously shown that oligomers containing mixtures of α- and β-amino acid residues ("α/β-peptides") can mimic the α-helix secondary structure, and that properly designed α/β-peptides can bind to proteins that evolved to bind to α-helical partners. Here we report fundamental studies that support the long-range goal of extending the α/β approach to tertiary structures. We have evaluated the impact of single α → β modifications on the structure and stability of the small and well-studied villin headpiece subdomain (VHP). The native state of this 35-residue polypeptide contains several α-helical segments packed around a small hydrophobic core. We examined α → β substitution at four solvent-exposed positions, Asn19, Trp23, Gln26 and Lys30. In each case, both the β(3) homologue of the natural α residue and a cyclic β residue were evaluated. All α → β(3) substitutions caused significant destabilization of the tertiary structure as measured by variable-temperature circular dichroism, although at some of these positions, replacing the β(3) residue with a cyclic β residue led to improved stability. Atomic-resolution structures of four VHP analogues were obtained via quasiracemic crystallization. These findings contribute to a fundamental α/β-peptide knowledge-base by confirming that β(3)-amino acid residues can serve as effective structural mimics of homologous α-amino acid residues within a natural tertiary fold, which should support rational design of functional α/β analogues of natural poly-α-peptides.
- Department of Chemistry and ‡Department of Bacteriology, University of Wisconsin-Madison , Madison, Wisconsin 53706, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: