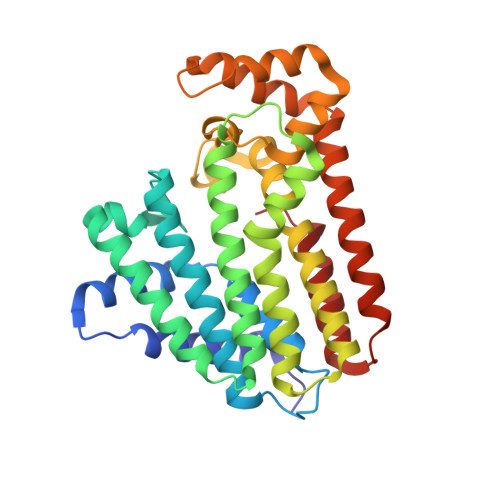
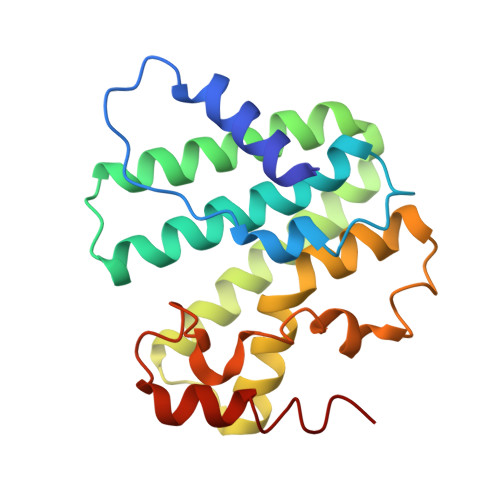
Structure, Function, and Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus Heptaprenyl Diphosphate Synthase
Desai, J., Liu, Y.L., Wei, H., Liu, W., Ko, T.P., Guo, R.T., Oldfield, E.(2016) ChemMedChem 11: 1915-1923
- PubMed: 27457559
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201600311
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5H9D - PubMed Abstract:
We report the first structure of heptaprenyl diphosphate synthase from Staphylococcus aureus (SaHepPPS), together with an investigation of its mechanism of action and inhibition. The protein is involved in the formation of menaquinone, a key electron transporter in many bacteria, including pathogens. SaHepPPS consists of a "catalytic " subunit (SaHepPPS-2) having two "DDXXD" motifs and a "regulatory" subunit (SaHepPPS-1) that lacks these motifs. High concentrations of the substrates, isopentenyl diphosphate and farnesyl diphosphate, inhibit the enzyme, which is also potently inhibited by bisphosphonates. The most active inhibitors (Ki ∼200 nm) were N-alkyl analogues of zoledronate containing ∼C6 alkyl side chains. They were modestly active against S. aureus cell growth, and growth inhibition was partially "rescued" by the addition of menaquinone-7. Because SaHepPPS is essential for S. aureus cell growth, its structure is of interest in the context of the development of menaquinone biosynthesis inhibitors as potential antibiotic leads.
- Center for Biophysics and Quantitative Biology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 1110 West Green Street, Urbana, IL, 61801, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: