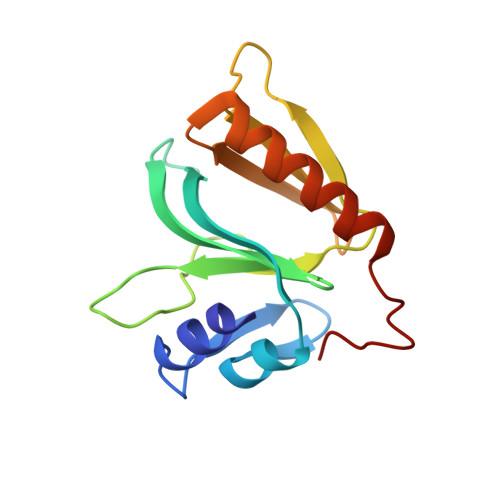
Crystal structure of hGEF-H1 PH domain provides insight into incapability in phosphoinositide binding
Jiang, Y., Jiang, H., Zhou, S., Meng, B., Liu, Z.J., Ouyang, S.(2016) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 471: 621-627
- PubMed: 26820534
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.01.150
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5EFX - PubMed Abstract:
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor GEF-H1 (also known as ARHGEF2) is identified as a member of the Dbl family of GEFs. It regulates RhoA-dependent cell signaling pathways and plays important roles in biological processes. GEF-H1 contains an N-terminal zinc finger domain, a Dbl-homologous (DH) domain followed by a Pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, and a C-terminal domain. The specific roles of its PH domain are poorly understood. Here we report the crystal structure of human GEF-H1 PH domain to 2.45 Å resolution. A conserved surface is formed by β8, β9, β10, and it may mediate protein-protein interactions. Although the folding resembles other PH domains that have defined structures, superposition of different PH domains clearly shows that the loop between β6/β7 and the loop between β3/β4 are so close that they will prevent its binding with phosphoinositide due to steric hindrance, and this has been proved by isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) and thermal shift assay (TSA). Our studies provide a structural framework for further work on the function of GEF-H1.
- National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China.
Organizational Affiliation: