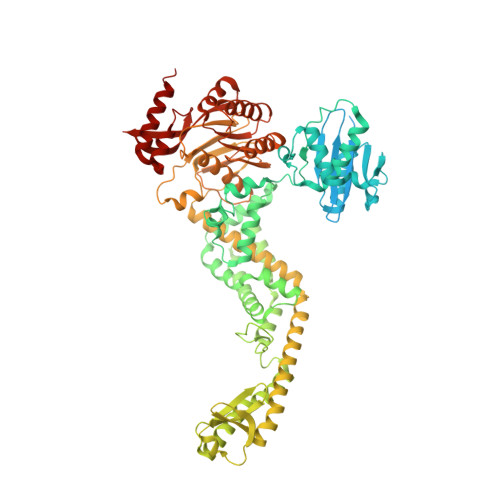
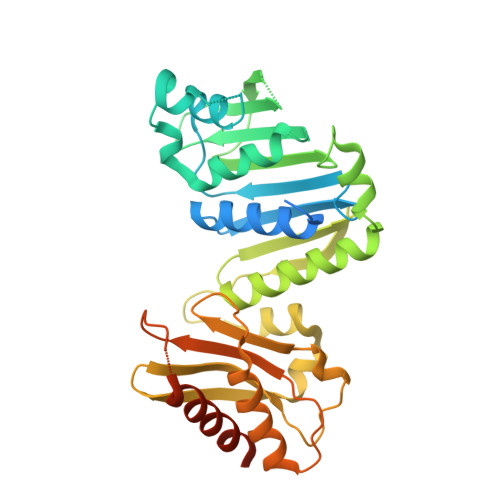
MutS/MutL crystal structure reveals that the MutS sliding clamp loads MutL onto DNA.
Groothuizen, F.S., Winkler, I., Cristovao, M., Fish, A., Winterwerp, H.H., Reumer, A., Marx, A.D., Hermans, N., Nicholls, R.A., Murshudov, G.N., Lebbink, J.H., Friedhoff, P., Sixma, T.K.(2015) Elife 4: e06744-e06744
- PubMed: 26163658
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.06744
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5AKB, 5AKC, 5AKD - PubMed Abstract:
To avoid mutations in the genome, DNA replication is generally followed by DNA mismatch repair (MMR). MMR starts when a MutS homolog recognizes a mismatch and undergoes an ATP-dependent transformation to an elusive sliding clamp state. How this transient state promotes MutL homolog recruitment and activation of repair is unclear. Here we present a crystal structure of the MutS/MutL complex using a site-specifically crosslinked complex and examine how large conformational changes lead to activation of MutL. The structure captures MutS in the sliding clamp conformation, where tilting of the MutS subunits across each other pushes DNA into a new channel, and reorientation of the connector domain creates an interface for MutL with both MutS subunits. Our work explains how the sliding clamp promotes loading of MutL onto DNA, to activate downstream effectors. We thus elucidate a crucial mechanism that ensures that MMR is initiated only after detection of a DNA mismatch.
- Division of Biochemistry and CGC.nl, Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, Netherlands.
Organizational Affiliation: