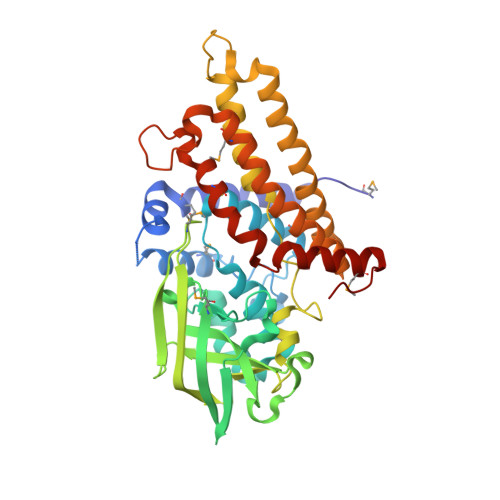
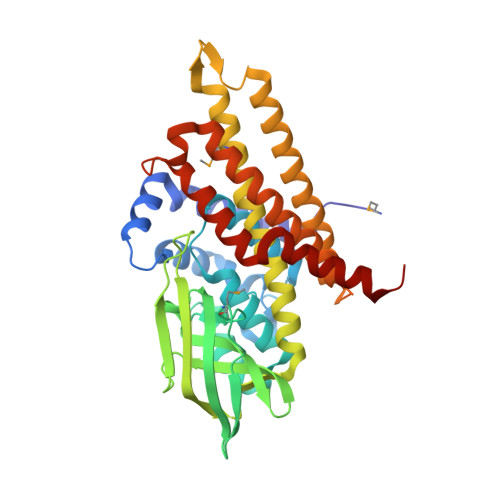
Unraveling Cholesterol Catabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: ChsE4-ChsE5 alpha 2 beta 2 Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Initiates beta-Oxidation of 3-Oxo-cholest-4-en-26-oyl CoA.
Yang, M., Lu, R., Guja, K.E., Wipperman, M.F., St Clair, J.R., Bonds, A.C., Garcia-Diaz, M., Sampson, N.S.(2015) ACS Infect Dis 1: 110-125
- PubMed: 26161441
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/id500033m
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4X28 - PubMed Abstract:
The metabolism of host cholesterol by Mycobacterium tuberculosis ( Mtb ) is an important factor for both its virulence and pathogenesis, although how and why cholesterol metabolism is required is not fully understood. Mtb uses a unique set of catabolic enzymes that are homologous to those required for classical β-oxidation of fatty acids but are specific for steroid-derived substrates. Here, we identify and assign the substrate specificities of two of these enzymes, ChsE4-ChsE5 (Rv3504-Rv3505) and ChsE3 (Rv3573c), that carry out cholesterol side chain oxidation in Mtb. Steady-state assays demonstrate that ChsE4-ChsE5 preferentially catalyzes the oxidation of 3-oxo-cholest-4-en-26-oyl CoA in the first cycle of cholesterol side chain β-oxidation that ultimately yields propionyl-CoA, whereas ChsE3 specifically catalyzes the oxidation of 3-oxo-chol-4-en-24-oyl CoA in the second cycle of β-oxidation that generates acetyl-CoA. However, ChsE4-ChsE5 can catalyze the oxidation of 3-oxo-chol-4-en-24-oyl CoA as well as 3-oxo-4-pregnene-20-carboxyl-CoA. The functional redundancy of ChsE4-ChsE5 explains the in vivo phenotype of the igr knockout strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ; the loss of ChsE1-ChsE2 can be compensated for by ChsE4-ChsE5 during the chronic phase of infection. The X-ray crystallographic structure of ChsE4-ChsE5 was determined to a resolution of 2.0 Å and represents the first high-resolution structure of a heterotetrameric acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (ACAD). Unlike typical homotetrameric ACADs that bind four flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) cofactors, ChsE4-ChsE5 binds one FAD at each dimer interface, resulting in only two substrate-binding sites rather than the classical four active sites. A comparison of the ChsE4-ChsE5 substrate-binding site to those of known mammalian ACADs reveals an enlarged binding cavity that accommodates steroid substrates and highlights novel prospects for designing inhibitors against the committed β-oxidation step in the first cycle of cholesterol side chain degradation by Mtb .
- Department of Chemistry, Department of Pharmacological Sciences, and Biochemistry and Structural Biology Graduate Program, Stony Brook University , Stony Brook, New York 11794, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: