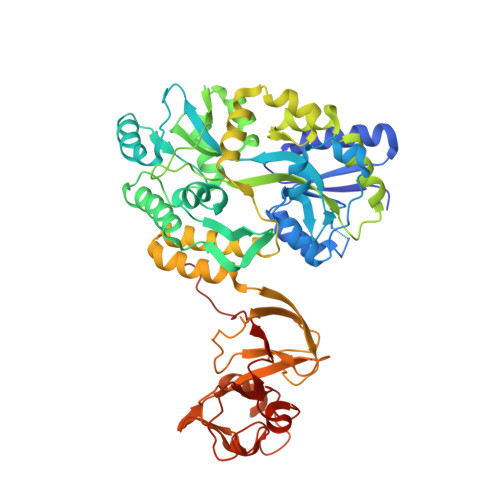
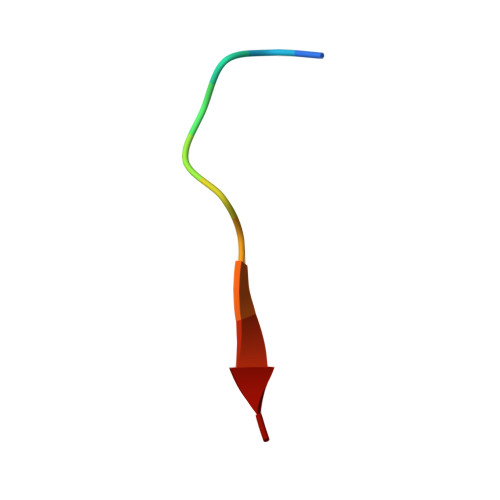
Peptide binding to a bacterial signal peptidase visualized by peptide tethering and carrier-driven crystallization.
Ting, Y.T., Harris, P.W., Batot, G., Brimble, M.A., Baker, E.N., Young, P.G.(2016) IUCrJ 3: 10-19
- PubMed: 26870377
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2052252515019971
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4WVG, 4WVH, 4WVI, 4WVJ - PubMed Abstract:
Bacterial type I signal peptidases (SPases) are membrane-anchored serine proteases that process the signal peptides of proteins exported via the Sec and Tat secretion systems. Despite their crucial importance for bacterial virulence and their attractiveness as drug targets, only one such enzyme, LepB from Escherichia coli, has been structurally characterized, and the transient nature of peptide binding has stymied attempts to directly visualize SPase-substrate complexes. Here, the crystal structure of SpsB, the type I signal peptidase from the Gram-positive pathogen Staphylococcus aureus, is reported, and a peptide-tethering strategy that exploits the use of carrier-driven crystallization is described. This enabled the determination of the crystal structures of three SpsB-peptide complexes, both with cleavable substrates and with an inhibitory peptide. SpsB-peptide interactions in these complexes are almost exclusively limited to the canonical signal-peptide motif Ala-X-Ala, for which clear specificity pockets are found. Minimal contacts are made outside this core, with the variable side chains of the peptides accommodated in shallow grooves or exposed faces. These results illustrate how high fidelity is retained despite broad sequence diversity, in a process that is vital for cell survival.
- School of Biological Sciences, The University of Auckland, Auckland 1142, New Zealand; Maurice Wilkins Centre for Molecular Biodiscovery, The University of Auckland, Auckland 1142, New Zealand.
Organizational Affiliation: