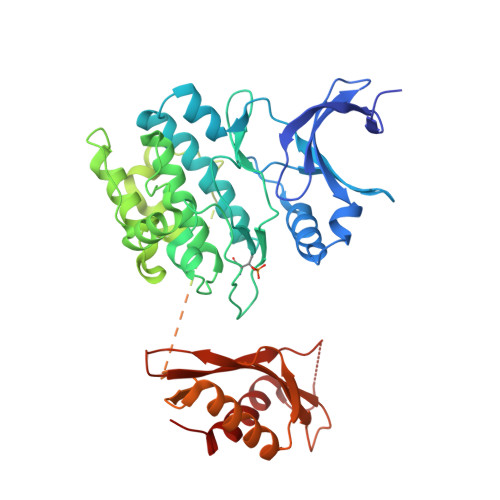
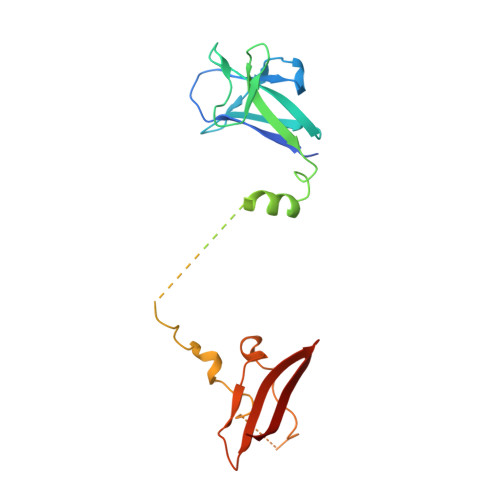
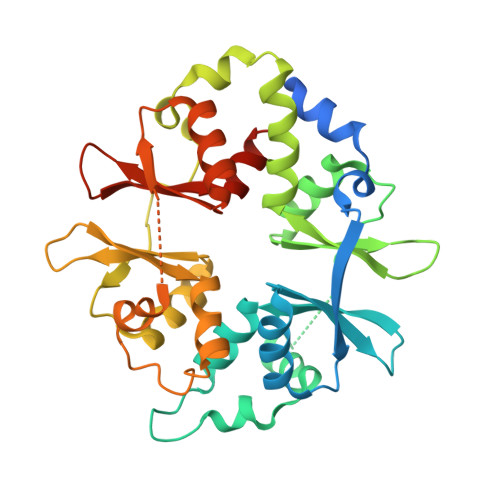
Structural Basis for AMPK Activation: Natural and Synthetic Ligands Regulate Kinase Activity from Opposite Poles by Different Molecular Mechanisms.
Calabrese, M.F., Rajamohan, F., Harris, M.S., Caspers, N.L., Magyar, R., Withka, J.M., Wang, H., Borzilleri, K.A., Sahasrabudhe, P.V., Hoth, L.R., Geoghegan, K.F., Han, S., Brown, J., Subashi, T.A., Reyes, A.R., Frisbie, R.K., Ward, J., Miller, R.A., Landro, J.A., Londregan, A.T., Carpino, P.A., Cabral, S., Smith, A.C., Conn, E.L., Cameron, K.O., Qiu, X., Kurumbail, R.G.(2014) Structure 22: 1161-1172
- PubMed: 25066137
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2014.06.009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4QFG, 4QFR, 4QFS - PubMed Abstract:
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a principal metabolic regulator affecting growth and response to cellular stress. Comprised of catalytic and regulatory subunits, each present in multiple forms, AMPK is best described as a family of related enzymes. In recent years, AMPK has emerged as a desirable target for modulation of numerous diseases, yet clinical therapies remain elusive. Challenges result, in part, from an incomplete understanding of the structure and function of full-length heterotrimeric complexes. In this work, we provide the full-length structure of the widely expressed α1β1γ1 isoform of mammalian AMPK, along with detailed kinetic and biophysical characterization. We characterize binding of the broadly studied synthetic activator A769662 and its analogs. Our studies follow on the heels of the recent disclosure of the α2β1γ1 structure and provide insight into the distinct molecular mechanisms of AMPK regulation by AMP and A769662.
- Worldwide Research and Development, Pfizer Inc., Eastern Point Road, Groton, CT 06340, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: