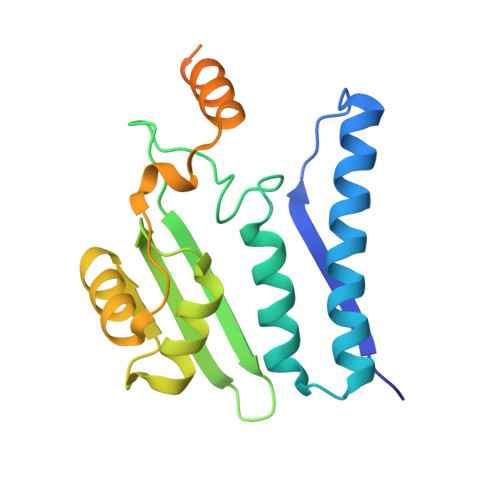
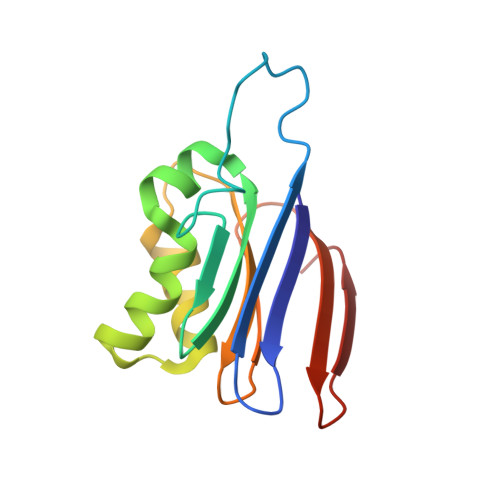
Na+/K+ exchange switches the catalytic apparatus of potassium-dependent plant L-asparaginase
Bejger, M., Imiolczyk, B., Clavel, D., Gilski, M., Pajak, A., Marsolais, F., Jaskolski, M.(2014) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70: 1854-1872
- PubMed: 25004963
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004714008700
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4PU6, 4PV2, 4PV3 - PubMed Abstract:
Plant-type L-asparaginases, which are a subclass of the Ntn-hydrolase family, are divided into potassium-dependent and potassium-independent enzymes with different substrate preferences. While the potassium-independent enzymes have already been well characterized, there are no structural data for any of the members of the potassium-dependent group to illuminate the intriguing dependence of their catalytic mechanism on alkali-metal cations. Here, three crystal structures of a potassium-dependent plant-type L-asparaginase from Phaseolus vulgaris (PvAspG1) differing in the type of associated alkali metal ions (K(+), Na(+) or both) are presented and the structural consequences of the different ions are correlated with the enzyme activity. As in all plant-type L-asparaginases, immature PvAspG1 is a homodimer of two protein chains, which both undergo autocatalytic cleavage to α and β subunits, thus creating the mature heterotetramer or dimer of heterodimers (αβ)2. The αβ subunits of PvAspG1 are folded similarly to the potassium-independent enzymes, with a sandwich of two β-sheets flanked on each side by a layer of helices. In addition to the `sodium loop' (here referred to as the `stabilization loop') known from potassium-independent plant-type asparaginases, the potassium-dependent PvAspG1 enzyme contains another alkali metal-binding loop (the `activation loop') in subunit α (residues Val111-Ser118). The active site of PvAspG1 is located between these two metal-binding loops and in the immediate neighbourhood of three residues, His117, Arg224 and Glu250, acting as a catalytic switch, which is a novel feature that is identified in plant-type L-asparaginases for the first time. A comparison of the three PvAspG1 structures demonstrates how the metal ion bound in the activation loop influences its conformation, setting the catalytic switch to ON (when K(+) is coordinated) or OFF (when Na(+) is coordinated) to respectively allow or prevent anchoring of the reaction substrate/product in the active site. Moreover, it is proposed that Ser118, the last residue of the activation loop, is involved in the potassium-dependence mechanism. The PvAspG1 structures are discussed in comparison with those of potassium-independent L-asparaginases (LlA, EcAIII and hASNase3) and those of other Ntn-hydrolases (AGA and Tas1), as well as in the light of noncrystallographic studies.
- Center for Biocrystallographic Research, Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, Polish Academy of Sciences, Poznan, Poland.
Organizational Affiliation: