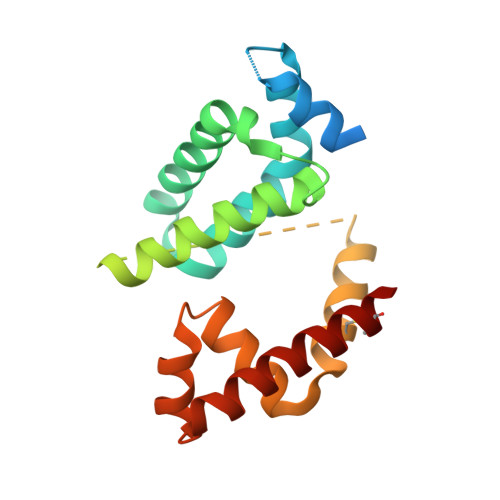
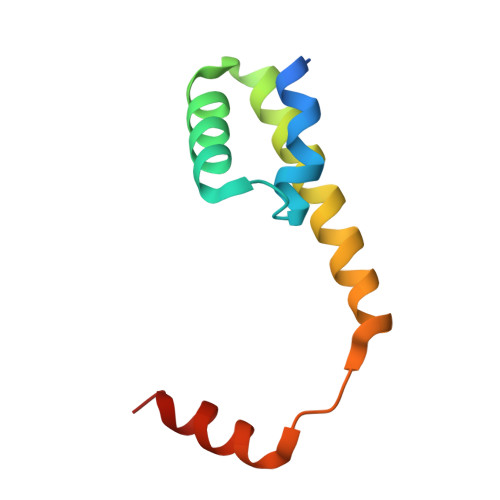
Structural basis for the redox sensitivity of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis SigK-RskA sigma-anti-sigma complex
Shukla, J., Gupta, R., Thakur, K.G., Gokhale, R., Gopal, B.(2014) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70: 1026-1036
- PubMed: 24699647
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004714000121
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4NQW - PubMed Abstract:
The host-pathogen interactions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection are significantly influenced by redox stimuli and alterations in the levels of secreted antigens. The extracytoplasmic function (ECF) σ factor σ(K) governs the transcription of the serodominant antigens MPT70 and MPT83. The cellular levels of σ(K) are regulated by the membrane-associated anti-σ(K) (RskA) that localizes σ(K) in an inactive complex. The crystal structure of M. tuberculosis σ(K) in complex with the cytosolic domain of RskA (RskAcyto) revealed a disulfide bridge in the -35 promoter-interaction region of σ(K). Biochemical experiments reveal that the redox potential of the disulfide-forming cysteines in σ(K) is consistent with its role as a sensor. The disulfide bond in σ(K) influences the stability of the σ(K)-RskAcyto complex but does not interfere with σ(K)-promoter DNA interactions. It is noted that these disulfide-forming cysteines are conserved across homologues, suggesting that this could be a general mechanism for redox-sensitive transcription regulation.
- Molecular Biophysics Unit, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560 012, India.
Organizational Affiliation: